All cardiovasc Flashcards
(284 cards)
What three factors determine CO?
CO = SV x HR
where SV is a function of preload and contractility
What kind of drug is clopidrogel? Use?
antiplatelet - adjunctive in pts w/ CAD, ischemic neuro syndromes, or stenting. PO.
Discuss pathology of the following stages of cardiac ischemia
- 20 - 30 mins
- 24 h
- 1-3 d
- 3-7 (10) days
- 20 - 30 mins: reversible ischemia (angina)
- 24 h: cut surface pallor
- 1-3 d: mottling w/ yellow-tan infarct ctr
- 3-7 (10) days: sharply outlined w/ central pale, yellowish necrotic region
Pattern of a Mobitz II 2nd degree AV block?
Same PR int. for each cycle w/ blocked P waves.
Calcific aortic stenosis
- one of most common valvular probs
- congenital biscuspid valve –> aging degeneration of valve w/ calcification
Major complications (3) of infective endocarditis?
- valve dest
- abscesses
- purulent pericarditis
histologic findings of giant cell myocarditis
myocyte necrosis and numerous giant cells
How do PDEi’s work (give rep. drug)
PDEs (milrinone) also increase contractility (similar to B1 agonists) but by inhibiting PDE thus keeping cAMP levels hi within myocytes.
What hemydynamic finding correlates best w/ RH failure?
Prominent RA v waves
Complete AV canal defect
- Describe (give 3 morphological features)
- Assoc. w/ what genotype
- Generally has complete mixing of ventricular contents due to defects in septation (endocardial cushions) – It is characterized by a primum atrial septal defect (ASD) that is contiguous with a posterior (or inlet) ventricular septal defect (VSD), and a common AV valve
- Assoc. w/ T-21.
What is a major problem w/ Eisenmenger’s syndrome? What is the goal of corrective surg for shunts?
- Once Eisenmenger’s sets in, surg is contraindicated and outcomes much worse
- Corrective surg: goal is to avoid dev’t of Eisenmenger’s
Temporal (Giant Cell) arteritis
- How common
- Symptoms
- Biopsy consideration
- Common complications
- Rx
- Most common vasculitis
- Headaches, scalp tender, jaw pain, visual loss
- A segmental dz so at least 2-3 cm of artery needed
- rapid response cort’s
What are the ANCA+ dz’s we learned?
- pANCA+
- cANCA+
- pANCA = hypersens. vasculitis (in 70% of pts)
- cANCA = granulomatosis w/ polyangiitis
What are 2 diff’s b/t PAN and hypersens. vasculitis?
- Hypersens = smaller vessels than PAN
- Lesions in hypersens at same stage of dev’t (as opposed 2 PAN)
Primary use of Type II CCB’s? HOw does this differ from Type I?
These are vasodilators used more for HTN control, and generally don’t have electrophysiological (cardiac) effect. Type I used more for cardiac, and cause electrophys. changes.
Infarction zones based on LAD, RCA or left circumflex?
- LAD: anterior wall LV
- RCA: post. wall LV + post septum
- Left Circ: lateral wall LV
Typical pathology of bacterial myocarditis?
Infectious foci w/ PMNs and bacteria
What are some causes of impaired DIA filling (leading to DIA heart failure)?
As these advance to HF, comment on the EF you might see.
Impaired DIA filling
- LV hypertrophy (Ao stenosis, HTN)
- Restrictive cardiomyopathy (amyloid, sarcoid, hemochromatosis, etc.)
- Pericardial constriction (constrictive pericarditis, cx, etc.) / tamponade
Hallmark dz of restrictive cardiomyopathy? Other big players in this condition?
amyloid; hemocrhomatosis/siderosis, sarcoidosis
Primary medical Rx of aortic regurg? Surg?
afterload reduction (nifedipine - CCB, ACEi)
surg: AVR
What are some of the key S/S of HF?
Decreased CO leading to:
- fatigue
- increased pulmonary venous pressure (exertional dyspnea, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea)
- increased systemic venous pressure (lower extremity edema)
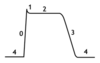
Dichrotic notch
Brief uptick in aortic pressure after the AV valve closes (after S2) due to recoil pressure following vent. contraction.
What are hallmark EKG signs in RBBB?
- wide QRS (>120ms)
- rSR’ in V1 (a tall “rabbit ear” secondary R wave in V1)

Claudication
limb angina: Pain in calf, thigh or buttock after some excercise; generaly resolves w/ rest.