All encompassing Flashcards
(913 cards)
List 4 presenting psychological symptoms of excessive alcohol consumption?
- Depression - Anxiety - Insomnia - Memory problems - Dementia
Why do you get a short PR interval in wolf parkinson white syndrome?
Presence of an accessory pathway known as the bundle of kent which can help with the conduction down to the ventricles
How does carbamazepine work?
It increases the GABA mediated inhibitory transmission in the CNS thus dec electrical excitibality
How to distinguish between episcleritis and scleritis - what test can you do?
Instillation of phenylephrine will not blanch the scleral vessels = scleritis. Episcleritis = mild pain, photophobia, red eye.
Pt presents with unilateral, localised, circumscribed bleeding in one eye. No inflammation, pain or discharge. Vision unchanged. Differential?
Subconjunctival haemorrhage (assoc with minor injuries, anticoags and anti platelets)
What are sulphonylureas contraindicated in?
- ketoacidosis
- acute porphyrias
What investigations are you going to do to a pt presenting with a goitre?
- TFTs
- USS for nodules
- CXR/thoracic inlet (tracheal compressions, retrosternal involvement)
- fine needle aspiration
Most common cause of Addison’s disease?
80% is due to AI. TB is most common worldwide.
what is the most common source of ectopic ACTH production in ectopic cushing’s syndrome?
small cell lung cancer
When a pt brings in a newspaper article into the OSCE what method are you going to use to help analyse the paper?
PECOS
- patient/participant/people
- Exposure/event/experimental interventin
- Comparison
- Outcome
- Study design
A 65-year-old man presents with chest pain radiating to the jaw. The ECG shows ST segment elevation in II, III and aVF, with T-wave inversion in V5 and V6.
Inferior MI
Causes of a headache worse in the morning?
- Cluster - raised ICP
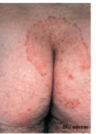
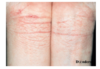
What is this? term and assoc condition?

Excoriations - loss of epidermis following trauma. Eczema
List 4 SE of ipratropium bromide?
- Dry mouth
- headache
- tachycardia
- urinary retention
- ocular effects
Causes of large bowel obstruction?
- colon cancer
- sigmoid volvulus
- diverticular disease
How does insulin lower plasma glucose?
- stimulate glucose transport into fat and muscle cells
- inhibit gluconeogensis & lipolysis
- stimulate glycogen synth
Pt presents, lean, tanned, tired and tearful with some diarrhoea. Differential?
Addison’s disease. +/- weakness, GI disturbances, mood changes, postural hypotension.
What type of angina is provoked by vivid dreams and can wake a pt up at night?
Nocturnal angina. Critical Coronary artery disease
Pt presents complaining of visual floaters?
retinal detachment - painless loss of vision. Grey area of retina where retina is detached seen on fundoscopy.
What is Murphy’s sign used to test for?
Cholecystitis
What type of prevention is it when the prevention of clinical diseases is due to early detectiong and screening?
- secondary
What are the four core features of depression?
- other common features?
- Somatic features?
- What else should you ask about in a depression history?
Core features
- low mood
- loss of interest
- tired all the time
- Anhedonia
Other common features (3 P’s)
- Poor concentration
- Poor self esteem and self confidence
- guilt & pessimism
Somatic
- sleep disturbances (early morning waking)
- morning depression
- loss libido
- loss of apetite/wt loss
- social withdrawal
- Anxiety, hallucinations, delusions, mania
- Suicidal risk (and risk to others)
Pt presents with pain around the sub mandibular gland esp when eating. Also swelling, palpable hard lump. Diagnosis?
Sialolithiasis
Would the urine sodium levels be elevated in pre renal or intrinsic causes of acute renal failure?
Intrinsic causes = the tubules are damaged so cannot reabsorb the sodium therefore you piss more of it out.