all that remains Flashcards
(28 cards)
4 major classes of ‘macromolecules’
- Nucleic acids – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) 2. Proteins 3. Lipids (“Fat”) 4. Carbohydrates (“Sugar”)
Nucleic acids and the ‘central dogma’
The central dogma of molecular biology deals with the detailed residue by-residue transfer of sequential information. It states that such information cannot be transferred back from protein to either protein or nucleic acid.
brief interruptions in the supply of glucose and oxygen to the brain can cause ________.
irreparable damage to the brain. (stroke)
why dont octopi have a blind spot?
the optic nerve directly attaches to the back of the retina
are Neuropsychiatric diseases very heritable?
highly heritable
Ependymal cells
coat the brains ventricles
What causes Depolarization?
an influx of Na+ ions into the cell through newly-opened Na+-channels,
What causes repolarization?
efflux of K+-ions.
The membrane potential at rest.
- High relative potassium conductance keeps the membrane potential near EK. 2. Very little/no Na+ can flow 3. The sodium-potassium keeps the concentration gradient difference high
The membrane potential after opening sodium channels.
- We stipulate that the conductance of Na+ is much higher than K+ 2. Because of the large driving force, Na+ rushes into the cell (high Ina) 3. This brings the membrane potential closer to ENa(+62mV), because positive ions are moving inside the cell, counteracting the negative resting membrane potential.
The membrane potential after closing sodium channels.
- Na+ channels close 2. Membrane conductance is returned to the baseline condition (gK > gNa) 3. Because there’s much more K+ inside than outside the cell, potassium is driven out through still open channels until Vm = EK, or -80mV
Larger axons carry action potentials _______ and depolarize ________.
Faster More quickly
Meninges
protects CNS
Spinal cord
transmits information between CNS/PNS,spinal reflexes – Dorsal roots: afferent sensory information into the CNS. – Ventral roots: efferent information from the CNS to the periphery (i.e. motor)
Brainstem
Diencephalon hind brain mid brain
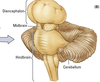
Diencephalon
Hypothalamus: Critical regulator of hormonal and instinctual behaviors.( • Thalamus: Relay station for sensory input to brain.
hind brain
• Pons: Bridge between cerebellum/rest of brain, voluntary movement regulation. • Medulla: Regulator of instinctual movements like breathing and heart rhythm regulation. • Cerebellum: Motor control
mid brain
• Tectum (dorsal): Visual and auditory input to colliculi superior and inferior • Tegmentum (ventral): motor regulation via small nuclei e.g. red nucleus and substantia nigra
spinal nerves
Communicate between nervous system and the body, dorsal = sensory and ventral = motor
Cranial nerves
communicate with structures mostly in the head and neck.
Large synapses can cause _____ changes in the post-synaptic membrane potential.
larger
Amino acid and amine neurotransmitters are released from…? Peptide neurotransmitter molecules are released from ?
synaptic vesicles. secretory granules.
Ligand-gated ion channels
comprised of 4-5 subunits that physically contain a pore that allows ions to cross the membrane in response to neurotransmitter binding.
Metabotropic receptors
they do not open a pore after binding to their neurotransmitter. Rater, they act via “G-proteins’, located on the inside face of the cell membrane.






