Anaemia -CVR Flashcards
(41 cards)
what demographic of people can have symptoms of anaemia even though their Hb and Hct are normal?
Those with chronic respiratory disease and those with malnutrition

what are the most common SYMPTOMS of anaemia
Dyspnea WITH exertion and AT REST
Fatigue
Hyperdynamic state like bounding pulses
what are the boundaries for microcytic, normocytic or macrocytic anaemia?

what are the overall mechanisms of anaemia
*Yr 1*
- Reduced production of red cells/haemoglobin in the bone marrow
- Reduced survival of red cells in the circulation - haemolysis
- Loss of blood from the body
- Pooling of red cells in a very large spleen
what are the 4 main causes of Microcytic anaemia
Iron def anaemia
Thalassaemia (alpha and beta)
- Anaemia of chronic disease*
- sideroblastic*
For Iron deficiency anaemia, what are the parameters for:
- iron
- ferritin
- Transferrin or TIBC
- Transferrin sats
Ferritin- iron stores

what are the causes of IRON deficiency anaemia
People with chronic slow bleeding like:
- Heavy menstruation ore postmenopausal bleeding
- Colon cancer- rectal bleeding
Diet- vegans etc
Pregnancy
IBS
Celiac disease
H.pylori infection
Meds like NSAIDs or aspirin
GI symptoms like dysphagia, haematemesis, maleana

if a pt result shows iron deficiency anaemia, what investigations should perform to determine it’s causing?
- Feacal Immunochemical test for blood in the stool
- GI investigations like:
- Upper GI endoscopy
- Duodenal endoscopy
- Colonoscopy
- Coeliac antibody testing
what are the treatments of iron deficiency anaemia?
Oral iron supplements with orange juice: it can have S/E like nausea, diarrhoea
if the supplement isn’t tolerated then use IV iron
what are the results of the blood count, blood film and iron tests for a pt with Anaemia of chronic disease
ESR is high due to inflammation
MCV may be normal
Ferritin is high (body likes to store iron during systemic inflammation)

what are the common causes (diseases associated) of Anaemia of chronic disease?
Occur in people with:
- Infections like TB or HIV
- Rheumatoid arthritis or other autoimmune disorders like SLE
- Cancers
Hence anaemia of chronic disease will resolve once the underlying condition resolves.
it occurs with other disease
why is ferritin high in anaemia of chronic disease
In inflammatory states, hepcidin production is increased.
Hepcidin blocks the release of iron from liver and absorption fro GI

Describe the pathophysiology of Anaemia of chronic disease
Pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-1, IL-6 and TNFa are released
These cytokines:
- reduces erythropoietin
- stimulates the production of hepcidin

what is the blood results of thalassaemia
Everything is normal
Problem is with globin synthesis
Contrast the two types of thalassaemia and what are the severity of symptoms for each mutation
alpha- mutation in alpha chain (found in fetal and adult)
Beta- only found in adult haemoglobin
there are 4 alpha genes and 2 beta genes

what are the treatment for thalassaemia?
blood transfusion
Iron chelating agents (sweep iron away through faces or urine)
Pts with thalassaemia present with it from brith
Summarise sideroblastic anaemia
There is too many sideroblasts (in bone marrow)
The unused iron build up in blood and bind to trasnferrin
A ring is seen on blood film (iron-binding to mitochondria)

what are the causes of sideroblastic anaemia and what is the result of bone marrow biopsy?
what is the treatment
Congenital
Acquired:
- alcohol, copper or Vit b6 def
- myelodysplastic syndrome
BM biopsy: ringed sideroblasts
Treatment depends on the cause

One of the causes of macrocytic anaemia is Megaloblastic anaemia.
what are the results of it on a blood film.
Macrocytes
Hypersegmented neutrophils
what is the mechanism underlying formation of megaloblasts in megaloblastic anaemia?
Impaired DNA synthesis,
Hence impaired nuclear maturation and cell division
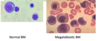
what are the causes of Megaloblastic anaemia
Most common are; Vit B12 and/Or Folate deficiency
Others are secondary to agents or mutations that impair DNA synthesis like:
- Drugs: azathioprine, cytotoxic chemotherapy
- Folate antagonists: methotrexate
- BM cancers: myelodysplastic syndrome
what are the importance of Vitamin B12 and folate
Vit B12
- DNA synthesis
- The integrity of the nervous system- hence can cause neurological symptoms if deficient.
Folic acid is required for
- DNASynthesis
- Homocysteine metabolism

When b12 or folate test is not conclusive enough, what other tests can you do to discern the cause of megaloblastic anaemia
Homocysteine and Methylmalonic acid

what are the causes of Vit B12 deficiency and give corresponding treatments?
B12 can be stored for years
N.B: Test for pernicious anaemia using anti IF antibody test or endoscopy)













