Anatomy Lecture 2 -- Posterior Abdominal Wall Flashcards
(50 cards)
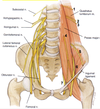
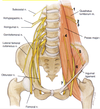
Upper attachments of the psoas major
- Sides of vertebrae T12 to L5
- IV discs
- Transverse processes

Lower attachment of the psoas major
Lesser trochanter of the femur with iliacus muscle (iliopsoas)

Upper attachment of the psoas minor
- Sides of vertebrae T12 to L1
- IV discs
- Transverse processes

Lower attachment of the psoas minor
Superior ramus of the pubic bone (pectineal line)

Posterior abdominal wall muscles that cross under the inguinal ligament
- Psoas major
- Iliacus
Posterior abdominal wall muscle that passes over the inguinal ligament
Psoas minor
Upper attachment of the quadratus lumborum
- Medial 1/2 of inferior border of the 12th rib
- Transverse processes of L1 to L5

Lower attachment of the quadratus lumborum
- Iliolumbar ligament
- Iliac crest

Upper attachments of the iliacus
- Superior 2/3 of iliac fossa
- Ala (wing) of sacrum
- Anterior sacroiliac ligaments

Lower attachment of the iliacus
Tendon of psoas = iliopsoas

5 muscles of the posterior abdominal wall
- Psoas major
- Psoas minor
- Quadratus lumborum
- Iliacus
- Transversus abdominus
3 origins of the muscle fibres of the diaphragm
- Sternum
- Ribs (costal margin)
- Lumbar vertebrae
Diaphragmatic muscle that wraps around the esophagus
Right crus

Diaphragmatic muscles on either side of the aorta
Right and left crus

Nerve that travels alongside the IVC. How does its corresponding nerve pierce the diaphragm?
- Right phrenic nerve
- Left pierces diaphragm on its own
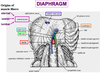
Where do the muscle fibres of the diaphragm converge?
Central tendon
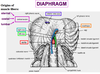
Ligament of the diaphragm that forms the hole through which the aorta enters
Median arcuate ligament
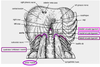
Ligament of the diaphragm that lets the psoas pass underneath
Medial arcuate ligament

Ligament of the diaphragm that lets the quadratus lumborum come through
Laterla arcuate ligament

Define the caval foramen
Hole in the central tendon through which the right phrenic nerve and lymphatics pass

How does the sympathetic trunk pierce the diaphragm
On either side of the abdominal aorta just inside the medial arcuate ligament

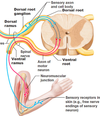
Define somatic nerves
Any nerve that is not in the gut (i.e. arms, legs and body wall; motor and sensory)
Define a reflex arc
A neural circuit that creates a more or less automatic link between a sensory input and a specific motor output

Describe how the simplest spinal reflexes are mediated
3 element chain:
- Sensory neurons
- –> interneurons in the spinal cord
- –> motor neurons
(–> means activate)