Anatomy of the biliary tract and the spleen Flashcards
(41 cards)
Name the gut associated organs
Liver
Gallbladder
Pancreas
Spleen
How is bile produced?
Produced by hepatocytes
Secreted into canaliculi
Canaliculi join to enter bile ductules and ducts in the portal triad.
Label the lobule


What type of epithelium are ductules and ducts made of?
Ductules = cuboidal epithelium
Ducts = columnar epithelium
Complete the diagram of the biliary tree


What is the structure of the biliary tree?
Smaller ducts continuously join together.
Liver, gallbladder and pancreas secretions enter the duodenum.
Where are the Hepatic, Cystic and Bile Ducts?
Left and right hepatic ducts leave via porta hepatis.
-Join to form the common hepatic duct.
Cystic ducts joins to form the common bile duct.
Complete the diagram on the biliary tree


What is the structure of the Extrahepatic Bile Duct?
Duct wall now contains fibrous connective tissue and smooth muscle.
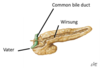
Meets the pancreatic duct to form the (hepatopancreatic) ampulla of Vater.
Finally, the sphincter of Oddi moderates emptying into the duodenum.
What are the anatomical relations of the bile duct and portal triad?
Anatomical relations in this area are a crucial surgical consideration.
Bile duct is anterior to the portal vein.
Bile duct is to the right of the hepatic artery.
Label the portal triad


What are the functions on the gallbladder?
●Store and concentrate bile
●Selectively absorb bile salts
●Excrete cholesterol and mucous
What is bile?
Bile is an important digestive fluid which emulsifies fats.
What is the gross anatomy of the gallbladder?
Characteristically conical/pear-shaped.
Divided into the fundus, body and neck
Where is the gallbladder located?
Located on the inferior surface of the right lobe of the liver.


Blockages of the biliary tree can occur and inhibit the movement of bile to the duodenum. Which of the following is most likely to worsen symptoms related to a blockage such as this?
A.Emotional stress
B.Heavy exercise
C.Ingesting fatty foods
D.Pregnancy
E.Smoking
C.Ingesting fatty foods
Where is the pancreas?
Located posterior to the stomach
What is the function of the pancreas?
Exocrine and endocrine gland
- Exocrine: secrete digestive enzymes into the duodenum
- Endocrine: secretes hormones such as insulin
What is the pancreas divided into?
Divided into the head, body and tail.
What supplies the pancreas (artery, vein and nerve)?
Arteries - Splenic, Coeliac trunk, pacreaticduodenal
Veins - Pancreatic (drain into the portal vein)
Nerves: Coeliac ganglia and Vagus
Label the pancreas


What is the exocrine pathway of the pancreas?
- Pancreatic secretions collect in small ducts
- These ducts join to form the Wirsung
- The Wirsung meets the common bile duct to form the hepatopancreatic ampulla / ampulla of Vater
- This then empties into the duodenum at the major duodenal papilla