Anesthesia Consultation Flashcards
(67 cards)
What is the purpose of the preoperative consultation?
To reduce the patient’s surgical and anesthetic perioperative morbidity or mortality, and to return the patient to desirable level functioning as quickly as possible.
“Perioperative risk” is multifactorial and a function of: (3)
- the preoperative medical condition of the patient
- the invasiveness of the surgical procedure
- the type of anesthetic administered
Surgical procedures and administration of anesthesia are associated with a complex stress response that is proportional to: (4)
- the magnitude of injury
- total operating time
- amount of intraoperative blood loss
- degree of postoperative pain
What is the key factor in improving outcome and lowering the length of hospital stay as well as the total costs of patients care?
Decreasing the stress response to surgery and trauma
What are the goals of preoperative evaluation?
- Documentation of the condition(s) for which surgery is needed.
- Assessment of the patient’s overall health status.
- Uncovering of hidden conditions that could cause problems both during and after surgery.
- Perioperative risk determination.
- Optimization of the patient’s medical condition in order to reduce the patient’s surgical and anesthetic perioperative morbidity or mortality.
- Development of an appropriate perioperative care plan.
- Education of the patient about surgery, anesthesia, intraoperative care and postoperative pain treatments in the hope of reducing anxiety and facilitating recovery.
- Reduction of costs, shortening of hospital stay, reduction of cancellations and increase of patient satisfaction.
What is the most important component of the preoperative evaluation?
patient history
What should the patient history include? (8)
- a past and current medical history
- a surgical history
- a family history
- a social history (use of tobacco, alcohol and illegal drugs)
- a history of allergies
- current and recent drug therapy
- unusual reactions or responses to drugs and any problems or complications associated with previous anesthetics.
- family history of adverse reactions associated with anesthesia should also be obtained.
A focused pre-anesthesia physical examination includes: (2)
- an assessment of the airway
- lungs and heart, with documentation of vital signs
When is a complete blood count needed? (4)
- major surgery
- chronic cardiovascular, pulmonary, renal, or hepatic disease, or malignancy
- known or suspected anemia, hemorrhage, or myelosuppression
- less than 1 y/o
When is an PTT/INR indicated? (3)
anticoagulant therapy
bleeding diathesis (hemorrhage)
liver disease
When are electrolytes and creatinine labs indicated? (5)
HTN
renal disease
diabetes
pituitary or adrenal disease
digoxin or diuretic therapy
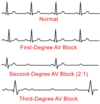
An EKG is indicated prior to surgery for these patients:
- heart disease, HTN, diabetes
- other risk factors for cardiac disease (including age, which alone is reason to get an ECG)
- subarachnoid or intracranial hemorrhage, CVA, head trauma
When is a CXR indicated preoperatively?
cardiac or pulmonary disease
malignancy
When should MAO be withdrawn prior to surgery?
Why?
2-3 weeks
risk of interactions with anesthetics
When should oral contraceptives be discontinues before elective surgery?
Why?
6 weeks
increased risk of venous thrombosis
When should patients discontinue their herbal supplements?
2 weeks prior
When should aspirin be discontinued prior to surgery?
7-10 days
When should thienopyridines (such as clopidogrel) be discontinued prior to surgery?
Why?
2 weeks before
Affects platelets
When should oral anticoagulants be discontinued prior to surgery?
What should INR level be?
4-5 days
1.5
What are major clinical predictors of increased risk for perioperative cardiac complications? (5)
recent MI
unstable or severe angina
decompensated CHF
significant arrhythmias
severe valvular disease
What are intermediate clinical predictors of increased risk for perioperative cardiac complications? (5)
mild angina
prior MI history
compensated CHF
diabetes
renal insufficiency
What are minor clinical predictors of increased risk for perioperative cardiac complications? (6)
advanced age
abnormal ECG
rhythm other than sinus
poor functional capacity
history of stroke
uncontrolled HTN
What are high risk predictors for perioperative cardiac complications? (cardiac complication rate of >5%) (4)
emergency surgery
aortic and major vascular surgery
prolonged surgical procedures with large fluid shifts or blood loss
unstable hemodynamic situations
What are intermediate risk procedures for perioperative cardiac complications? (cardiac complication rate of 1-5%) (6)
abdominal or thoracic surgery
neurosurgery
ENT procedures
minor vascular surgery
orthopedic surgery
prostatectomy