Anti-Inflammatory Corticosteroids Flashcards
(39 cards)
Effects of Glucocorticoids on Carbohydrate Metabolism
Gluconeogenesis, increase in blood glucose leading to insulin release, and glycogen synthesis with deposition in the liver
Effect of excess glucocorticoids on carbohydrate metabolism
Diabetes-like state
Effect of Glucocorticoids on Protein Metabolism
Increased aminoacid uptake from liver and kidney, decreased protein synthesis (except in liver), result is a net transfer of AAs from muscle/bone to liver
Effect of excess glucocorticoids on protein metabolism
Muscle wasting, catabolism of skin and connective tissue
Effect of Glucocorticoids on Lipid Metabolism
Net effect is lipogenesis due to increased insulin release. There is a greater lipogenic effect in the central tissues.
Effect of excess glucocorticoids on lipid metabolism
Centripetal obesity, buffalo hump and increased abdominal fat.
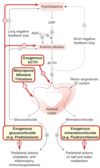
What is the physiologic mechanism of action of mineralcorticoids?
Aldosterone binds cytosolic receptor, migrates to nucleus where it increased translation of specific proteins: Na-K-ATPase, sodium channels, and potassium channels.
Physiologic effect of mineralcorticoid
Increased reabsorption of sodium from renal distal tubules, and increased secretion of protons and potassium.
What are therapeutic doses of corticosteroids generally used for?
Suppress inflammatory and immune responses. Most useful if the host response is the cause of deleterious effects of the disease.
Anti-Inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids
Decreased production and action of cytokines, reduced generation of leukotrienes and prostaglandins via decreased expression of COX-2 and inhibition of Phospholipase-A2.
Immunosuppressive effects of glucocorticoids
Reduction in chronic inflammation and autoimmune reactions BUT decreased healing and protective aspects of the immune system
How do glucocorticoids enact their immunosuppressive effects?
Suppress T-cell activation, suppress cytokine production, prevent mast cells and eosinophils from releasing chemical mediators
Effects of glucocorticoids on vascular events
Decreased vasodilation, decreased fluid exudation
Effects of glucocorticoids on cellular events
Overall decrease in accumulation and activation of cells
Mineralocorticoid activity refers to…
The salt (Na+)-retaining actions at the kidney.
Glucocorticoid activity refers to…
The metabolic effects: hyperglycemia, protein wasting, and lipid redistribution.
Compare the anti-inflammatory potency to the salt-retaining potency of cortisol (aka hydrocortisone)
1 : 1. i.e. Cortisol defines the potency. Just know Cortisol does both and we compare everything else to it.
Compare the anti-inflammatory potency to the salt-retaining potency of aldosterone. (relative to cortisol)
0.3 : 3000 i.e. Aldosterone’s effect is essentially only salt-retaining.
Compare the anti-inflammatory potency to the salt-retaining potency of Prednisone, Triamcinolone, and Dexamethasone. (relative to cortisol)
4-30 : 0-0.3 i.e. a lot of anti-inflammatory effect with little to no salt-retaining effect. Good choice to suppress immune system without mineralcorticoid activity.
Compare the anti-inflammatory potency to the salt-retaining potency of Fludrocortisone. (relative to cortisol)
10 : 125-250 i.e. a lot of salt-retaining effect with little immunosuppression.
Where is 11ß-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 (11ß-HSD1) expressed? And what reactions does it catalyze?
Liver. Converts cortisone to the active cortisol or prednisone to the active prednisolone. i.e. activating step.
Where is 11ß-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 (11ß-HSD2) expressed? And what reactions does it catalyze?
Kidney. Converts cortisol to cortisone or prednisolone to prednisone i.e. inactivating step.
Can you treat a pregnant woman with glucocorticoids without effect on the fetus?
Yes, because fetus expresses the inactivating enzyme (11(beta)-HSD2) in the kidney but does not express the activating enzyme (11(beta)-HSD1) in the liver i.e. it can convert the drug back to the prodrug. (assumption is you don’t saturate the inactivating enzyme)
Clinical considerations for use of Cortisol (aka Hydrocortisone)
Common use in physiologic doses for replacement therapy and emergencies; glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid actions [1:1]; administered orally and parenterally