AS Chemistry Bonding Flashcards
(27 cards)
What is ELECTRONEGATIVITY?
The ability of an atom to attract the bonding pair of electrons in a covalent bond
What is the most electronegative element?
Fluorine with a value of 4 on the Pauling Scale

What happens to electrons in a covalent bond with atoms with the same electronegativity?
Electrons are shared equally between the two bonding atoms
Does this form a polar bond?

No, this is a non-polar bond

What happens to electrons in a covalent bond with atoms with of different electronegativity
The electrons are attracted to the more electronegative element.
Does this form a polar bond?

- Yes, this is a polar bond
- A dipole is formed between the two atoms
- A dipole is a difference in charge between the two atoms

What do the following symbols mean on the HF molecule?

They show the charge separation on the moleucle
H is slightly positive
F is slightly negtative

List the 3 types of intermolecular forces from strongest to weakest
- Hydrogen bonding
- Dipole-dipole
- van der Waals
What type of substances are van der Waals forces found in?
- Atoms and molecules
- For example
–Helium, neon
–methane
Are van der Waals forces permanent or temporary?
•temporary
How are van der Waals forces caused?
- Electron in the orbitals are always moving
- At any particular moment they could be more on one side than the other
- At this moment, they have a temporary dipole
What do temporary dipoles cause in neighbouring atoms?
- This dipole can cause another temporary dipole in the opposite direction on a neighbouring atom
- The two dipoles are then attracted to each other
- This can then cause another dipole in another atom…like a domino effect

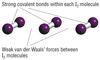
Which atom will have the greatest van der Waals forces and why?
F2 or I2?
- I2, more electrons….
- In solid I2, this forms a molecular lattice
What type of intermolecular forces do polar molecules have?
Permanent dipole-dipole forces

Hydrogen bonding only happens when hydrogen is bonded to ….?
- Fluorine
- Nitrogen
- Oxygen
- Because these are very electronegative and draw the electrons towards themselves
- Hydrogen also has a very high charge density because it is so small
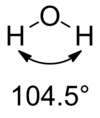
Draw the hydrogen bonds in water

What effect does hydrogen bonding have on the boiling point of water and why?
- Increases boiling point
- Each water molecule can hydrogen bond to 4 other hydrogen molecules
- So more energy required to break these hydrogen bonds to vaporise the water
What effect does hydrogen bonding have on the density of ice and why?
- Ice is less dense than water…which is why ice floats in water!
- Hydrogen bonds are relatively long
- So the molecules in ice are further apart, making ice less dense
What is a dative (or coordinate) covalent bond?
- Both electrons in the bond come from the same atom in the bond
- One atom will need to donate a lone pair of electrons
Show how an ammonium ion is formed

what is the shape of a molecule that has 3 bonding electron pairs on the central atom
•example: BF3
- 3 bonding electron pairs on the central atom
- Trigonal planar

What is the shape of the molecule with 2 bonding electron pairs on the central atom?
•BeCl2
•Bond angle 180O LINEAR

- What is the shape of a molecule with 4 bonding bonding electron pairs on the central atom
- CH4
•tetrahedral

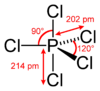
- What is the shape and bond angle of a molecule with 5 bonding bonding electron pairs on the central atom?
- PCl5
- Trigonal Bipyramidal
- 90O and 120O