Asthma & COPD Flashcards
(35 cards)
Name a systemic corticosteroid
methylprednisolone
Name an aerosol corticosteroid
fluticasone
Name a beta2 adrenergic agonist that is short acting?
albuterol
Name a beta2 adrenergic agonist that is long acting?
salmeterol
Name a short-acting muscarinic antagonist
ipratropium bromide
Name a long-acting muscarinic antagonist
tiotropium
Name a methylxanthine phosphodiesterase inhibitor
theophylline
Name a leukotriene pathway inhibitor
montelukast
Name an IgE inhibitor
omalizumab
What is the main mechanism for maintenance drugs?
**prevent **asthma attacks . . . they affect
airway responsiveness/reactivity
Which group of drugs affect airway resistance?
quick relief meds, relieve bronchoconstriction
What is the deposition of inhaled drugs?
Particles too small will come right back out.
Those that are too big will be swallowed.
2-5 micrometers = optimal and will be inhaled

Which are the most effective sites to pharmacologically target to prevent asthma attacks?
CS, IgE, leukotriene inhibitors >> neutrophils
muscarinic antagonists, B2 agonists, methylxanthines >> cholinergic reflex, bronchoconstriction
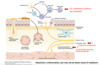
What is the most effective treatment in **preventing **asthma attacks?
inhaled glucocorticoids (ICS)
ICS suppress inflammation . . . DO NOT CURE disease.
In hrs, antiinflammatory effect; maximal benefit weeks/mo. Add B2 agonist before raising steroid dose.
True/False: 17 alpha substitution increases the topical activity of corticosteroids.
True.
Why?
How do corticosteroids suppress inflammatory gene transcription?
Recall: the corticosteroid gets translocated to the nucleus where it directly affects gene translation (stops acetlyation).

Name the effects of corticosteroids on airway cells
*corticosteroids increase the transcription of beta 2 receptors

What are two main adverse affects with corticosteroids?
inhalation >> oropharyngeal candidiasis and dysphonia
high dose/systemic >> HPA suppression (bone resorption, skin thinning, growth retardation)
When are systemic glucocorticoids used?
with asthma exacerbations
- short term 3-10 days, must withdraw over 1-2 weeks
When do you use B2 agonists in asthma?
short acting: rescue
long acting: + ICS
*most asthmatics can be controlled with ICS + B2 agonist
NOTE: B2 agonists increase glucocorticoid nuclear translocation (complement each other)
Bronchodilators

What is the difference between albuterol and salmeterol?
albuterol
- short acting 3-5 min
- peak 30-60 min
- duration 3-6 hr
- *salmeterol**
- duration >12 hr
MOA of B2 agonists

When do you know that asthma is not adequately controlled?
Using rescue inhaler >2x/week




