Asthma Management in Adults Flashcards
(36 cards)
Why is asthma therapy important?
It is common
Manageable
Dangerous
Expensive
What is wrong with the asthmatic airway?
Wall inflamed and thickens
Tightened smooth muscle

What are some of the symptoms of asthma?
Shortness of breath
Wheeze
Cough
Chest tightness
Diurnal variability
Episodic
Atopy
What does diurnal mean?
During the day
What are some of the signs of asthma?
Wheeze on auscultation
Eczema
Obstructed spirometry
PEF changes
Response to treatment
What is the complete control of asthma defined as?
No datime symptoms
No time-time awakening due to asthma
No need for rescue medication
No asthma attacks
No limitations on activity including exercise and normal lung function
Minimal side effects from medication
What does non-pharmacological management of asthma include?
Patient education and self-management plans
Exercise
Smoking cessation
Weight management
Flu/pneumococcal vaccinations
What does the pharmacological management of asthma include?
Inhaled therapy
Oral therapy
Specialist treatment
What kind of dosage to inhalers deliver?
Small dose
Where do inhalers deliver the drug to?
Directly to the target organ (airways and lungs)
What are advantages of inhalers?
Directly deliver to target organs
Onset of effect is faster
Minimal systemic exposure
Systemic adverse effects less severe and less frequent
What are some different kinds of inhalers?
pMDI (metered dose inhalers)
pMDI with spacers
Dry powder inhalers (DPI)
Short acting B2 agonist (SABA) relievers
What does SABA stand for?
Short acting B2 agonist
What does DPI stand for?
Dry powder inhalers
What does pMDI stand for?
Metered dose inhalers
What drugs are used in short acting B2 agonists?
Salbutamol
Terbutaline
What kinds of inhalers is salbutamol used in?
MDI (metered dose inhalers)
DPI (dry powder inhalers)
What kind of inhalers is terbutaline used in?
Dry powder inhalers
What kind of inhaler is this?
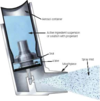
pMDI
What kind of inhaler is this?

pMDI with spacer
What kind of inhaler is this?

Dry powder inhaler
What are examples of oral therapy?
Leukotriene receptor antagonist
Theophylline
Prednisolone
What are examples of specialist options?
Omalozumab (anti IgE)
Mepolizumad (anti interleukin-5)
Bronchial thermoplasty
Why is omalizumab useful?
Anti IgE



