Atherosclerosis/Vascular Disease Flashcards
(230 cards)
Triphasic wave form
- strong forward component of blood flow during systole
- short reversal of blood flow during early diastole
- low amplitude foward blood flow during remaining diastole (loses vacuum, going back)
INACTIVE - when exercise - both systolic and diastolic flow increase

Bernoulli’s
as speed of a moving fluid increass, pressure within fluid decreases (and speed increases)
75% - flow begins to decreases and pressure downstream decreases to form a pressure gradient

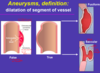
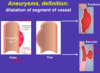
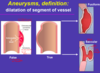
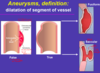
aneurysm vs diffuse ectasia
smaller increase generaly in diameter = de
aneurysm - widen, dilate (at least 50% increase over normal arterial diameter)
AAA
cystic medial degeneration - of elastic fibers
acuumulation of collagenous and mucoid material in the medial layer
mostly with aging and hypertension (marfan, ehlers danlos)
Type A Aortic Dissection
involves part of ascendinga aorta
surgical!
emergency and high mortality
lower BP in all

Type B Aortic Dissection
does not involve ascending aorta
complicated - surgical
uncomplicated - medical
AAA risk factors
increasing age
smoking
male
genetic
aortic wall tension
variation in wall tension in aneurysm
proportional to the product of pressure and radius
bigger radius = more tension = bigger chance of ruptiur
P is the same
AAA therapy
medican (smoking HTN)
endovascular/open therapy
PAD mechanism
if stenosis - high resistance
turbulent flow - pressure drops across stenosis and impaired endothelial function
inapility to increase flow with execise
mismatched O2 supply and demand (IC)
inefficient oxidation
can’t dilate because endothelial dysfunction - angina and claudation

claudication
cramping tightness aching fatigue
bluttock, hip, thigh, calf, foot
exercise induced
not with stating (relief)
less than 5 min
ABI
Under .90 is PAD!
measure P in both arms and legs
put highest angle P over highest arm P on eich side
add 2 numbers together
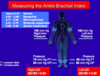
Toe Brachial Pressure
divide te pressure by higher of the two brachial ressures
when ABI not possible because calcified
PAD therapy
exercise
smoking cessation
STATINS
HTN
antiplatelets
symtomatic relief
revascularization (if gangrene, non healing ulcers, ischemic rest paid, bad claudication)
Raynauds Disease
rare disease that causes vasospasm of the arteries and reduces blood flow to fingers and toes
idiopathic or secondary (lupus, sjogrens)
vascular constriction - white/blue/numb extremities
Treatment for Raynauds Disease
CCBs
Alpha block
ARBs (vasodilate)
surgery (rare)
varicose veins
dilated tortuous veins
reflux bc valvular insufficiency
obesity, prenancy, familial
usually cosmetic - can be stasis dermatitis
Carotid artery disease therapy
can lead to stroke!
antiplatelet/anticoagulation
statins
risk factor modification (smoking, HTN, diabetes)
revascularization (stenting)
arteriovenous malformation
embryonic/fetal development
direct connections between arteries and veins! more common in brain or SC
risk factors for CAD
herediatry
lipids (high LDL)
smoking
diabetes
HTN
obesity
CRP
inflammation marker
predictor of first MI/ischemic stroke (also high if another stressor)
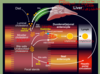
Atherosclerosis Pathway
- endothelial injury
- LDLs enter, smoooth muscle cells migrate
- macrophages roll and enter epithelial cell and eat LDL and turn into foam cell
- secrete cytokines to recruit more
- more macrophages enter - fatty streak
- TGF beta increases collagen
macrophages make MMP-9 which breaks down fatty cap

Thinning of fibrous cap
degraded by foam cells secreting MMP
rupture!!
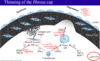
synthesis of fibrous cap
smooth muscle cless promote collagen and elastin