B1.4 Photosynthesis Flashcards
(32 cards)
Define photosynthesis
The process by which plants harness the energy from the sun and transfer this energy into a useable food source in the form of glucose that can be stored as starch
State the reactants of photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide & water
State the products of photosynthesis
glucose + oxgygen
Photosynthesis is an ‘……..’thermic reaction.
Endothermic
Endothermic means
a chemical reaction in which energy is transferred from the surrounding to the reacting mixture
State the word equation for photosynthesis?
carbon dioxide + water (+ light) ——> oxgyen + glucose
State the chemical equation for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H20 ( + light) ———> C6H12O2 + 6O2
Why are plants and some algae termed ‘producers’?
They are organisms that make their own food through the process of photosynthesis
Name the two main stages of photosynthesis?
- Light dependent
- Light independent
State what happens in the first stage of photosynthesis?
The first stage is the light dependent stage of photosynthesis where energy transferred from light is used to split water molecules into oxygen gas and hydrogen ions
State what happens in the second stage of photosynthesis?
The second stage is the light independent stage of photosynthesis where carbon dioxide gas combines with the hydrogen ions produced in stage 1 of photosynthesis to make glucose
What happens to the glucose produced in photosynthesis?
- Stored as starch - food store
- Used for respiration
- Stored in fruit as sucrose
- Used to build cellulose cell walls
- Combined with nitrogen to build protiens for grow and repair
- Biosynthesis into fats and oils for food and growth
How can you test for starch to prove photosynthesis has taken place?
- Place leaf in boiling water for 1 minute to kill it
- Place in boiling tube with ethanol
- Place boiling tube in a water bath an boil until white (chlorophyll removed)
- Wash leaf with water to remove ethanol and soften
- Place on white tile and add 1-2 iodine drops
- Watch for colour change in iodine.
How can a leaf be ‘destarched’ before a photosynthesis experiement?
Keep it in the dark for a minimum of 24 hours - starch present will be used up in respiration and without light no further glucose can be produced by photosynthesis to be converted to starch.
How do you prove chlorophyll is needed for photosynthesis?
- Take a variagated plant and destarch
- Place the destarched plant in sunlight for several hours
- Test oneof the leave with iodine for the presence of starch

How do you prove light is needed for photosynthesis?
- Take a destarched plant and cover part of one of its leaves with black card or tin foil
- Place the destarched plant in sunlight for several hours
- Remove and uncover the partially covered leaf
- Test the leaf that was partially covered with iodine for the presence of starch
How do you prove carbon dioxide is needed for photosynthesis?
- Take a destarched plant cover part of one of its leaves/stems with a conical flask or polythene bag containing soda lime
- Place the destarched plant in sunlight for several hours
- Remove one of the covered leaves and test with iodine for the presence of starch

How do you prove oxygen is given of during photosynthesis?
- Place an upturned funnel and test tube over an aquatic plant in a beaker of water
- Put the apparatus in the light for maximum photosynthesis
- Collect a full test tube of gas
- Place a glowing splint into the test tube to test for oxygen
- Relights = oxygen present
What is meant by a ‘limiting factor’?
Factors which can prevent an increase in the rate of photosynthesis
State the main limiting factors which affect the rate of photosynthesis?
- Light intensity
- Carbon dioxide availability
- Temperature
Which of the following is NOT a limiting factor of photosynthesis:
- Temperature
- Light intensity
- Amount of chlorophyll
- Carbon dioxide concentration
- volume of rain
volume of rain
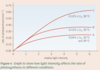
Describes the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis
As light intensity increases, the rate of photosynthesis increases until another limiting factor has an effect.
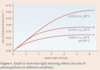
Describes the effect of temperature on the rate of photosynthesis?
As temperature increases, the rate of photosynthesis increases, up to a point and then any further increase in temperature decreases the rate of photosynthesis
Why does the rate of photosynthesis drop if the temperature gets too high?
The enzymes involved in photosynthesis have denatured