B16-18 Ecology Flashcards
(42 cards)
Define the term ecosystem.
An ecosystem includes all of the living things interacting with each other, and also with their non-living environment.

Give an Example of an Abiotic factor
Abiotic factors are the non living components of an ecosystem so things such as the soil pH, light levels, wind speed, water content etc.

Define a ‘Community’
A group of organisms or a population of different species occupying a particular area.

Name a producer on this food web

The Grass.
Name a secondary consumer on this food web.

snake or lizard
What are the mising labels on the water cycle? Starting with the arrows up from the sea to the sun and working clockwise.

Evaporation, Condensation, precipitation.
What is a detritovore?
An organism that eats detritus (decaying matter).

What is a saprophyte?
A fungus or plant which feeds on detritus by secreting enzymes which help digest the detritus.

Name a process which locks carbon away.
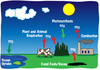
Photosynthesis or sedimentation
Name a process which adds carbon to the carbon cycle
Respiration or Combustion

What does ‘biodiverse’ mean?
An area with a large number of different species living there.

What is a pesticide?
A chemical which kills pests, used in farming methods.

What is a herbicide?
A chemical used in agriculture which kills weeds.

What can cause algal blooms in lakes and result in Eutrophication?

Fertilisers
Name a gas responsible for causing acid rain.
Sulpher or nitrogen oxides.

What produces sulphur dioxide responsible for acid rain?
Cars and factories.

Name an effect of acid rain on the environment.
Limestone buildings and grave stones worn away, trees die, lakes too acidic for fish to survive.

Name a fossil fuel
natural gas, coal, oil.

What effect does the action of destroying peat bogs have on the gases in the atmosphere?

Increases the amount of carbon dioxide.
Describe one effect of deforestation on the environment.

Destroys habitats
reduces biodiversity
disruption of food chains
Name a gas responsible for Global warming.

Carbon dioxide, Methane.
Biodiversity can be reduced by these things:
H
I
P
P
O
Habitat destruction
Invasive species
Pollution
Population Increase
Overharvesting
What are Trophic Levels?
TRIPLE ONLY
They are the feeding levels within a food chain.

What is a top or ‘Apex’ predator?
TRIPLE ONLY

A predator that has no predators of its own.












