B5.071 - GI Tubal Cancers COPY Flashcards
(107 cards)
describe adenocarcinoma in the esophagus
distal esophagus
arises from Barretts
more common than squamous
types of cancer in the stomach
adenocarcinoma (most common)
lymphoma (H. plyori)
neuroendocrine (MEN1)
gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST)

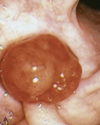
villous adenoma of colon with long sleder projections that are reminiscent of small intestinal villi
microscopic appearance of esoph squamou cell carcinoma
dysplastic/atypical squamous epithelium invading into submucosa or deeper
variably sized nests of tumor cells with epithelioid cells, ample eisinophilic cytoplasm, keratinization
describe lynch syndrome
pts do no have multiple polyps
often cancer at earlier age
follows microsattelite instablle pathway
germline mutations in mismatch repair proteins
precursor lesion for squamousc cell carcinoma of esophagus
squamous dysplasia, plaque like thickening
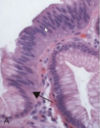
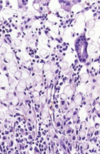
dysplasia in barretts esophagus
abrupt transition from barrett metaplasia to low grade dysplasia
note nuclear stratification and hyperchromasia
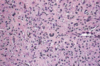
risk factors for carcinoid tumor
MEN-1, AMAG
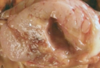
presentation of GIST
asymptomatic
sx due to mass effect when large, may ulcerate causing bleeding
diffuse type stomach adenocarcinoma features
gross: diffues thickening (linitis platsica)
micro: sheets of cells sometimes signet ring
associated with hereditary gastric cx
mutations in CDH1 (e-cadherin)
pts also have lobular breast cx
describe squamous cancer of esophagus
middle/upper esophagus
not assoicated with barretts
more common world wide
location of esophageal adenocarcinoma
distal 1/3 of esophagus
presentation of esophageal adenocarcinoma
long standing GERD
odynophagia or dysphagia
weight loss, vomiting. hematemesis
location and clinical presentation of squamous cell carcinoma of esophagus
mid esophagus or upper
dysphagia, odynophagia, obstruction
weight loss
what is a hyperplastic polyp
not considered a precursor to adenocarcinoma
microscopic shows serrated polyp without dilation at the base

neuroendocrine tumor
molecular features of GIST
most have activating mutation in KIT gene
some have activating mutation in PDGFRA
treatment with imatinib only works in tumors with mutations in these genes
risk factors for esoph squamous cell carcinoma
smoking, alcohol, esophageal injury, achalasia, frequent consumption of very hot beverages, radiation, lower SES
more common in iran, china, brazil, SA
pathogenesis of colon adenocarcinoma (2 pathways)
stepwise collection of multiple mutations
APD/beta catenin pathway
microsattelite instable pathway

GIST

barrett
architectural irregularities, including gland within glad or “cribiform” profiles in high grade dysplasia
risk factors for lymphoma
chronic inflammation, H. pylori (eradication of H pylori can resolve lymphoma in early stage)
intestinal type stomach adenocarcinoma features
gross: mass lesion, often ulcerated
micro: intiltrating atypical glands with mucin production
associated with intestinal metaplasia, FAP, H. pylori
describe barretts esophagus
replacement with columnar epithelium and goblet cells
resonse to repeated injury of reflux (10% of pts with GERD)
may develop dysplasia