Back Flashcards
(174 cards)
Identify

- C7
- medial scapula border
- spine of the scap
- inferior angle of the scap
- upper trap
Identify

- costovertebral angle (CVA)
- T12
- lower trap
- lumbar paraspinal muscles
- iliac crest
- L4 (level)
- PSIS
- sacrum
What are the 4 regions of the vertebrae?
- cervical
- thoracic
- lumbar
- sacrum/coccyx
What is the function of the spine?
absorb shock
What are primary curves?
kyphotic
What are secondary curves?
lordotic
When/why do the secondary curves develop?
- cervical - hold head/sit upright
- lumbar - stand/walk
What are the motions of the spine?
- flexion
- extension
- lateral flexion
- rotation
Which are the typical vertebrae?
C3-L5
(all but 1st two)
Identify
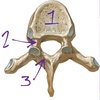
- body
- pedicle
- lamina
Identify

pedicles
Identify
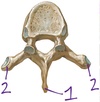
- SP (spinous process)
- TP (transverse process
Identify

- SP
- TP
What is the function of the SP & TP?
attachment and lever for spinal muscles
Identify

- superior articular process
- inferior articular process
Identify

- superior vertebral notch
- inferior vertebral notch
- intervertebral foramen
Identify

- vertebral foramen
Vertebral ______ collectively form the vertebral ______.
- foramina
- canal
Identify

- C1 (atlas)
- C2 (axis)
Helpful Hint: Atlas, the Greek god, holds up the world therefor C1 articulates with the occiput and it rotates on an axis(C2)
Identify
and
What view is this?

C1
- anterior arch
- anterior tubercle
- posterior arch
- posterior tubercl
- superior facet for articulation for occipital condyles
Superior view
Identify
and
What view is this?

C1
- posterior arch
- posterior tubercle
- anterior arch
- anterior tubercle
- inferior facet articulation for C2
Inferior view
Identify

- transverse foramen
- TP
Which are the atypical vertebrae?
- C1
- C2
Identify

dens





































































