basics Flashcards
(84 cards)
In Primary level of organization
(in protein structure) what is the:
Basis of structure and
Kinds of bonds and interaction
Amino acid sequence
Covalent peptide bonds
In QUATERNARY level of organization
(in protein structure) what is the:
Basis of structure and
Kinds of bonds and interaction
Association of 2 or more folded polypeptide to form a multimeric protein
Disulfide bond, H-bond, Ionic bond, Van der Waals interaction, hydrophobic interaction

Adenine
Purine





glycine (Gly)

Proline (Pro)

Cysteine (Cys)
Amino acids
that are Hydroxylated in mature collagen (2)
Proline
Lysine

Asparagine (Asn)
Small nuclear RNA (snRNA)
Components of spliceosomes involved with mRNA splicing
What Disaccharide?

Maltose
Saturated Fatty Acids
No double bonds
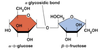
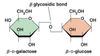
type of glycosidic bond in lactose
beta glycosidic bond

Lysine (Lys)
Terpenes
Formed from Isoprene
(Also called isoprenoids)

Aspartate (Asp)
Amino Acids:
Phosphorylation, O-linked glycosylation
Serine
Threonine
found in plants (starch)
alphs (1->4) bonds
Branched every 12-25 glucose units via a (1->6) bonds
side chain about 20-25 glucoses long
Amylopectin

Glutamate (Glu)
Type of glycosidic bond in
Maltose and sucrose
Alpha glycosidic bond
found in animal cells and some bacteria
Primary alpha (1->4) bonds
Highly branched every 8-10 glucose units via alpha (1->6) bonds
side chain about 8-12 glucoses long
Glycogen

Thymine
Pirimidines
found in plants bonds
beta (1->4) bonds
unbranched
Cellulose