Basics (Amino Acids, Proteins, Protein Analysis) Flashcards
(69 cards)
1 A = ___ m
1 Angstrom = 1 x 10-10 m
How big is the radius of an atom on avg?
1-2 Angstroms
1-2 x 10-10 m
What is the average size of a protein?
150 residues
30-50 Angstroms
Weight of 1 Hydrogen?
1 dalton
What is the average weight of an amino acid?
110 daltons
What is a covalent bond? How strong are they?
- A covalent bond is a bond in which electrons are shared between 2 atoms.
- They are strong (> 100 kcal/mol)
- Bring atoms close together (1-2 Angstroms)
Order of electronegativity for elements found in proteins?
O > N > C = S > H
What is electronegativity?
Ability of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond
What is a hydrogen bond?
Bond formed between an H atom in a polar bond such as O-H or N-H and an electronegative atom like O and N.
- Weak (1-3 kcal/mol)
- Contribute to protein structure and stability
Equation for pH
pH = -log[H+]
Define pKa
The pH at which the concentrations of HA and A- are equal
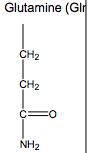
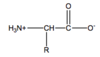
Describe the chemical structure of an amino acid in 2 parts
- Set of atoms that make up the backbone of the protein chain
- side chain atoms that make them unique
Basic structure of an Amino Acid?
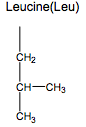
What are the Nonpolar Amino Acids?
Gly, Ala, Val, Leu, Ile, Met, Pro, Phe, Trp
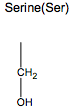
What are the uncharged but polar amino acids?
Asn, Gln, Ser, Thr, Tyr, Cys
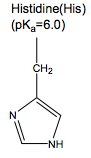
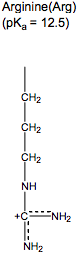
What are the charged and polar amino acids?
Arg, Lys, Glu, Asp, His
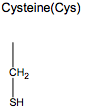
What is special about Cysteine?
- Can form covalent bonds (disulfide bonds) between 2 sulfurs
- Stabilize or constrain proteins
- Found in extracellular proteins
Which amino acid forms disulfide bonds that stabilize or ocnstrain proteins?
Cysteine
What is unique about Glycine?
- Glycine has no side chain
- Flexible, found in tight turns
What is unique about Proline?
- Side chain bonds to the nitrogen along the peptide backbone and forms a ring structure
- Rigidifies a protein
Gly

Ala

Val

Ile