BB Flashcards
(520 cards)
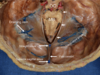
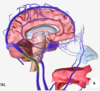
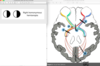
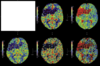
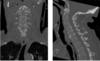
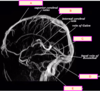
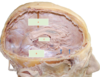
which of the following is the falx cerebri
A
B
C
D
E

which of the following is the falx cerebri
A
B
C
D
E
which area of the brain contains the primary motor cortex?
cerebellum
temporal
midbrain
occipital
frontal
which area of the brain contains the primary motor cortex?
cerebellum
temporal
midbrain
occipital
frontal
which of the following used air vibration as its mode of operation?
a) outer ear
b) middle ear
c) inner ear
d) central auditory NS
which of the following used air vibration as its mode of operation?
- *a) outer ear**
b) middle ear
c) inner ear
d) central auditory NS
which part of brain integrates sensory information?
cerebellum
temporal
midbrain
pariteal
occipital
which part of brain integrates sensory information?
cerebellum
temporal
midbrain
pariteal
occipital
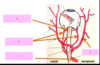
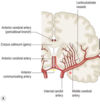
which of the following connects to the external carotid artery?
middle cerebral artery
anterior cerebral artery
posterior communicating artery
menigeal branch
opthalmic artery
which of the following connects to the external carotid artery?
middle cerebral artery
anterior cerebral artery
posterior communicating artery
menigeal branch
opthalmic artery
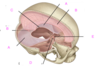
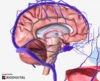
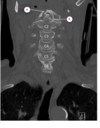
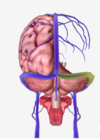
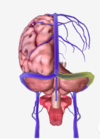
which of the following is the superior sagittal sinus?
A
B
C
D
E

which of the following is the superior sagittal sinus?
A
B
C
D
E
A 23-year-old man presents to his GP complaining of headaches and changes to his hearing. He describes unilateral hearing loss and tinnitus.
An MRI head diagnoses a vestibular schwannoma (acoustic neuroma). There are two cranial nerves responsible for these symptoms, as they both pass through the internal acoustic meatus.
Which of the following is one of the nerves affected?
Accessory
Facial
Labyrinthine
Trigeminal
Vagus
A 23-year-old man presents to his GP complaining of headaches and changes to his hearing. He describes unilateral hearing loss and tinnitus.
An MRI head diagnoses a vestibular schwannoma (acoustic neuroma). There are two cranial nerves responsible for these symptoms, as they both pass through the internal acoustic meatus.
Which of the following is one of the nerves affected?
Accessory
Facial
Labyrinthine
Trigeminal
Vagus
which of the following influences conciousness by modulating motivation and motor activity?
noradrenaline
ACh
serotonin
dopamine
adrenaline
which of the following influences conciousness by modulating motivation and motor activity?
noradrenaline
ACh
serotonin
dopamine
adrenaline
which of the following is attaches to the eyeball posterior to the eyeball equator?
superior rectus
inferior olbique
medial rectus
lateral rectus
superior oblique
what movement does this cause? [1]
which of the following is attaches to the eyeball posterior to the eyeball equator?
superior rectus
inferior olbique
medial rectus
lateral rectus
superior oblique
what movement does this cause? [1]
depression of eye
which hormone causes nausea?
insulin
ghrelin
leptin
GLP-1
CCK
which hormone causes nausea?
insulin
ghrelin
leptin
GLP-1
CCK
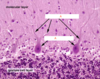
label A-C of (from the ear)

A: scala vestibuli
B: scala media
C: scale tympani
which of the lateral spinothalamic tracts causes unpleasant quality of painfulness?
PAG
mediodorsal nuclei of thalamus
ventromedial (VM) & ventroposterior (VP) of thalamus
which of the lateral spinothalamic tracts causes unpleasant quality of painfulness?
PAG
mediodorsal nuclei of thalamus
ventromedial (VM) & ventroposterior (VP) of thalamus
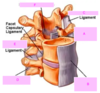
what are the type of joints found between adjacent verebral bodies?
synchondrosis
symphysis
synostosis
syndesmoses
what are the type of joints found between adjacent verebral bodies?
synchondrosis
symphysis
synostosis
syndesmoses
Symphysial joints are where the bones are united by a layer of fibrocartilage. They are slightly movable (amphiarthrosis).
which of the following is does not rise rapidly after a meal?
insulin
ghrelin
leptin
GLP-1
CCK
which of the following is does not rise rapidly after a meal?
insulin
ghrelin
leptin
GLP-1
CCK
which of the following applies to Glutamate?
- neurotransmitters only
- neuromodulator only
- neurotrophic factor only
- neurotransmitters & neuromodulator
- neurotransmitters, neuromodulator & neurotrophic factor
which of the following applies to Glutamate?
- neurotransmitters only
- neuromodulator only
- neurotrophic factor only
- *- neurotransmitters & neuromodulator**
- neurotransmitters, neuromodulator & neurotrophic factor
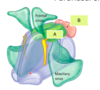
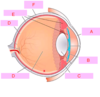
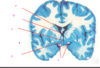
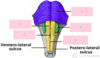
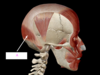
what is A?
infundibulum
falx cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
tentorial notch
falx cerebelli

what is A?
infundibulum
falx cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
tentorial notch
falx cerebelli

which of the following is the lateral ventricle?
A
B
C
D
E
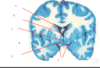
which of the following is the lateral ventricle?
A
B
C
D
E
where do you find the spinothalamic tract
pons
midbrain
medulla
where do you find the spinothalamic tract
pons
midbrain
medulla
which of the following is where internal cues (such as blood hormones are detected) when controlling hunger?
lateral hypthalamic nucleus
arcuate nucleus
periventricular nucleus
supraoptic nucleus
paraventricular nucleus
which of the following is where internal cues (such as blood hormones are detected) when controlling hunger?
lateral hypthalamic nucleus
arcuate nucleus
periventricular nucleus
supraoptic nucleus
paraventricular nucleus
which of the following provide physical & metabolic support for the neurons
oligodendrocytes
ependymal
astrocytes
microglial
schwann
which of the following provide physical & metabolic support for the neurons
oligodendrocytes
ependymal
astrocytes
microglial
schwann
what does this describe: ‘when a muscle is stretched, this change in length is transmitted to the spindles and their intrafusal fibers which are subsequently similarly stretched’ [1]
muscle length detector
which of the following transports information to the occipital lobe?
medial longitudinal fasciculi
lateral geniculate pathway
tectonate pathway
meyers loop
optic nerve
which of the following transports information to the occipital lobe?
medial longitudinal fasciculi
lateral geniculate pathway
tectonate pathway
meyers loop
optic nerve
which of the following best matches the afferent and efferent CNs for blink reflex
- afferent = CN 2, efferent = CN 3
- afferent = CN 2, efferent = CN 4
- afferent = CN 5, efferent = CN 3
- afferent = CN 5, efferent = CN 7
- afferent = CN 2, efferent = CN 7
which of the following best matches the afferent and efferent CNs for blink reflex
- afferent = CN 2, efferent = CN 3
- afferent = CN 2, efferent = CN 4
- afferent = CN 5, efferent = CN 3
* *4. afferent = CN 5, efferent = CN 7** - afferent = CN 2, efferent = CN 5
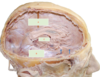
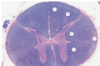
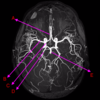
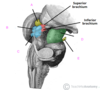
which of the following is the olive?
A
B
C
D
E

which of the following is the olive?
A
B
C
D
E