Biochemistry - MCAT Flashcards
(150 cards)
Pinocytosis can also be called what due to the fact that it ingests dissolved electrolytes and solvents?
cell drinking
Can urea diffuse across the membrane?
yes
Can an ion moving through an ion channel down its concentration gradient also be moving against an osmotic gradient?
yes
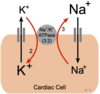
How many potassium (K) are pumped inside and sodium (Na) are pumped outside of the cell with NaK ATPase?
2, 3
Does phagocytosis take up solids or liquids?
solids
During the citric acid cycle, what form of energy is phosphorylated/is the energy product?
GTP
What molecules are oxidized in the electron transport chain?
NADH, FADH2
How many NET ATP are produced in glycolysis?
2
How many ATP are produced per NADH oxidized?
2.5
How many ATP are produced per FADH2 oxidized?
1.5
Does higher salt content in your sweat mean higher or lower salt content in your blood?
lower
If a molecule is reduced will it have more or fewer bonds to oxygen?
fewer
If a molecule likes to be reduced, will it have a higher or lower reduction potential?
higher
As you go across the ETC, each complex has a higher or lower reduction potential than the last?
higher
What glucose transporter is in nearly *all* tissues and increases when blood glucose is low? hint: “baseline”
GLUT1
What glucose transporter is on gluconeogenic cells, is bidirectional, and senses glucose on the pancreas?
GLUT2
What glucose transporter has a high glucose affinity even during low conc.? note: in brain and placenta
GLUT3
What glucose transporter is expressed at high glu conc because it stores glucose?
GLUT4
Where does glycolysis take place in the cell?
cytosol
Where does the citric acid cycle take place in eukaryotes?
mitochondrial matrix
Draw the graphs for competitive inhibitors
Vmax doesn’t change Km increases (binding affinity decreases bc more than one molecule is competing for binding site)

Draw the graphs for *noncompetitive* inhibitors
Binds allosterically and decreases the enzyme activity (Vmax) but binding affinity stays the same (no change to Km)

Draw the graphs for *uncompetitive* inhibitors
Binds allosterically and won’t let enzyme release the substrate (increases binding affinity/decreases Km), Vmax decreases bc less enzyme is left to work

What is the brain division for the forebrain called?
prosencephalon (personality and behavior)