BIOMED - Histology Flashcards
(41 cards)
What are the 2 physiologic divisions of the respiratory tracts and what are there functions?
Conducting: transporting air to where it can undergo gas exchange. Respiratory: gas exchange!
What cell type makes up respiratory epithelium?
Ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium w/ goblet cells
What are the main functions of the respiratory epithelium and the lamina propria?
Warm and humidify air Aid in immune response Trap particles in mucus and cilia to propel them out
What are the 4 layers of the trachea and what is generally found in each?
Starting from inner to outer: mucosa (epithelium and lamina propria) Submucosa (glands) Trachealis muscle / cartilage layer Adventitia (connective tissue)
Is the anterior or posterior region of the trachea more cartilaginous? And which is more muscular?
Anterior 2/3 is cartilage. Posterior 1/3 is trachealis muscle.
What type of cartilage will you find in the trachea?
Hyaline
The epithelial cells of the bronchus are __________ transitioning to _________.
Respiratory epithelium (as before, pseudostratified) Transitioning to simple columnar.
Smooth muscle is located in between what layers in the bronchus?
Just beyond the epithelial layer and superficial to the submucosa
How is the cartilage organized differently in the bronchus than it is in the trachea?
Cartilage is arranged in discs in the bronchus unlike in the trachea where it is a ring.
What part of the respiratory tract are Clara cells located and what is their function?
Lower respiratory tract, Bronchioles 1. Secretes a substance (surfactant) that decreases surface tension to prevent collapse of the airway (basically makes the lumen less sticky so it doesn’t stay stuck to itself and prevent an open airway). 2. Secretes substances which combat irritants. 3. Stem cells.
What are the 3 primary cell types of the alveoli? What are their functions and what do they look like?
Type I: minimum barrier to gas exchange and so they are squamous or flat in appearance. Type II: They produce and secrete surfactant, so they are cuboidal and between the junctions of 2 alveoli Dust Cells / alveolar macrophages: scavenge for particles that don’t belong in the alveoli - these are usually hanging out in the lumen.
What type of tissue is found in the lamina propria?
Lymph
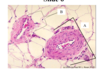
What is A, B, C?
What is this layer called?

A: Goblet Cells, which secrete mucus
B: Ciliated pseudostratified epithelial cells
C: basal stem cells
Respiratory Epithelium
What is A and what is it’s purpose?
What is D?
What is C and what is found here?
What layer is B and what can be found here?
What is E?
Where is this section from and how do we know?

Hyaline cartilage (which helps keep the airway open)
Respiratory epithelium
Lamina propia: lymph, blood vessels
Submucosa: contains ACH receptors (effect cilial mvmt and frequency), immunologic fx of serous/mucus glands
Adventitia
This is from the trachea because the hyaline cartilage is more ring-like than disc-like.
What type of tissue is *?
What tissue is at the arrow?
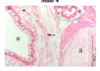
What part of the airway am I in and how do you know?

hyaline cartilage
smooth muscle
bronchi (most likely secondary), bc the cartilage is in discs, not a ring.
What layer is the arrow?
What layer is the pointer?
What is the *?
What is the tissue marked “a”?
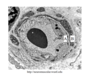
What structure is in the green circle?
What type of RE is present here?
Smooth muscle
lamina propia
lumen
discs of cartilage
glands!
columnar epithelium
What type of epithelium is found here?
Identify the structure marked by *
What is the structure marked by the pointer?
What is NOT present in this slide that helps us know where we are?
Where is this in the system?

Columnar, with some cuboidal
lamina propia
smooth muscle
no cartilage, no pseudostrat epithelium
So we are in the bronchioles!
What are the blue arrows?
What is the green arrow?
What level of the respiratory system is this slide taken from and how do I know?

Ciliated cuboidal epithelial cells
Clara cell
Bronchioles: clara cells, cuboidal cells, a complete absence of cartilage
What is the *?
What type of bronchiole is at the arrow head? What is the primary fx?
What type of bronchiole is at the arrow? What is the primary fx?

alveoli
respiratory - respiratory
terminal - last conducting portion
What type of cell is at the green arrow?
Blue arrow?
Red arrow?
What type of connective tissue is in alveolar walls and why?
What is in the black arrow and bracket and what does it do?

Type II alveolar cell - surfactant, stem cell
Type I alveolar cell - 90% of the SA of the alveoli, squamous to allow for easy gas exchange
Marcophage - immunity
Elastin, better for expansion and recoil
Port of Kohn, for communication and collateral circulation
If this a 58 year old man (a few months apart) with a chronic cough and a 60-70 pack year history admitted with SOB and lab values reading SPO2 88%, ph 7.34, PaCO2 60, HCO3 28, and PaO2 50 what are your conclusions regarding:
- What do the values indicate?
- What part of the lungs is affected?
- What differences might we expect to see between each?
- What disease is this?
- What parts of lung fx will be affected?
- What meds would be appropriate?
- What observations would we be looking at?

- He’s hypercapnic and hypoventilating.
- bronchi
- lamina propia is thicker, the epithelium has converted to stratified squamous which means there’s no cilia, glands, ducts which means we can’t get much mucus out)
- chronic bronchitis
- airway clearance, less things to combat infex, narrowing of the airway effects ventilation
- bronchodilator, corticosteroid
- blue bloater (cyanosis), use of accessory muscles to breathe / labored breathing, lots of coughing
8.
What pathology is this?

Emphysema
- What lobe is affected?
- What part of the lungs is affected?
- How would lung function be effected?
- What disease is this?
- What findings do we expect on physical exam?
- What meds are indicated?
- What PT interventions would you suggest for this patient?

- left lower
- alveoli
- no gas exchange, no air moving moving at all
- pneumonia
- abnormal breath sounds, fremitus (you’ll hear more one side when talking than the other bc the consolidation will resonate).
- antibiotics, bronchodilators, expectorant
- Chest PT
Name the 3 layers of the heart and vessels.
Tunica intima / endocardium
Tunica media / myocardium
Tunica Adventitia / epicardium
Vessels are on the left / the heart itself is on the right