Biopsychology Part One Flashcards
(34 cards)
What is Biopsychology?
application of principles of biology to the study of: -physiological -genetic -developmental mechanisms of behaviour
Label the parts of the brain shown here and name their primary functions

- Frontal Lobe: Anterior (front) portion > Personality/ Posterior (back) portion > Motor control
- Central Fissure : Separates prefrontal and postfrontal Gyri
- Parietal lobe: Sensation
- Lateral Fissure: Separates the frontal lobe and temporal lobe
- Temporal Lobe: Hearing
- Occipital Lobe: Vision
What is the function of the:
- PRE-CENTRAL gyrus
- POST CENTRAL gyrus?
- pre central gyrus: motor cortex
- post central gyrus: Somatosensory cortex
Label each of the parts of the brain:
- Fore brain:
- Telencephalon
- Diencephalon
- Midbrain:
- Mesencephalon
- Hindbrain:
- Metencephalon
- Myencephalon
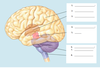
What structures are included in the Diencephalon (Forebrain) and what are their functions?
- Pituitary gland:“Master gland” produces hormones that act on other parts of the endocrine system
- Hypothalamus: regulates motivated behaviours (non-reflex) by controlling release of hormones from pituitary gland
- Thalamus: Major relay station for info to cortex
Name the structures of the Forebrain - Diencephalon shown below:

- Thalamus (dispatch! relay station to cortex)
- Hypothalamus (control hormones)
- Pituitary gland (hormone production)
What are Nuclei?
A cluster of densely packed cell bodies of neurons in the Central Nervous System
What are two important Nuclei of the hypothalamus and their functions?

- Mammilary bodies: Memory
- Pituitary gland: Hormone production
- Optic Chiasma : Vision
What are Ganglia?
Clusters of cell bodies in the PNS
What is a tract?
Bundles of axons in the CNS
What is a nerve?
Bundles of axons in the PNS
What is the somatic nervous system responsible for?
What kind of nerves is it made up of?
carries info to the CNS from the senses and from the CNS to the skeltal muscles
Afferent - sensory nerves
Efferent - motor nerves
What is the autonomic nervous system responsible for?
What kind of nerves is it made up of?
Regulating internal environment, carries info from the CNS to organs, blood vessels and glands
Sympathetic & Parasympathetic nerves >both are efferent (motor nerves),
also has afferent nerves (sensory)
What are two characteristics of the Sympathetic nervous system?
- “fight or flight response”
- second stage neurons are far from the target organ
What are two characteristics of the Parasympathetic nervous system?
- “Rest and restore”
- Second stage neurons are near to the target organ
How many cranial nerves are there?
Are they sensory or motor?
12 - both Autonomic (sympoathetic/parasympathetic) and Somatic (afferent/efferent)
sensory and motor components to most of them
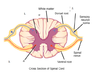
What are the three meninges encasing the CNS?
- Dura mater (tough)
- Arachnoid membrane (web-like)
- Pia mater (Adheres to CNS surface)
name the meninges shown below:
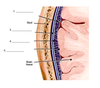
- Sub arachnoid space
- Dura mater
- Arachnoid mater
- Pia Mater
What are two main types of protection for the brain?
Chemical:
Blood-brain barrier > tightly packed cells of blood vessel walls prevent entry of molecules
Physical:
Skull, meninges, Cerbrospinal fluid
Label the follwing neuron components and types:

- Dendrites
- Cell body (soma)
- Axon
- Unipolar Neuron
- Bipolar neuron
- Multipolar neuron
- Multipolar neuron
What are glial cells?
What type are found in the CNS?
What type are found in the PNS?
Glial cells surround neurons and provide support as well as insulation
CNS: Oligodendrocytes (myelin sheath), astrocytes (blood-brain barrier), microglial cells (injury response)
PNS: Schwann cells (myelin sheath)
Which glial cells can regenerate?
PNS axons - Schwann cells can regenerate
What are the spaes between myelin called?
Nodes of Ranvier
Which are the most abundant CNS Neuroglia?
Astrocytes