Black & White Pathology Flashcards
(48 cards)
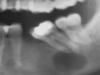
What is an area of hematopoietic bone marrow that produces a radiolucency, typically in the posterior mandible?
Focal Osteoporotic Marrow Defect
What are the characteristics of benign neoplasms of bone?
- asymptomatic
- slow growth
- expands the cortex instead of going through it
- symmetrical
- does not metastasize
What are characteristic of malignant neoplasms of bone?
- symptomatic
- grows faster
- invades/destroys structures like the cortex
- asymmetrical
- poorly defined margins
- deposits bone outside of cortex
- can metastasize
This is a benign (non-neoplastic) radiographic finding in a female. These are usually seen in the posterior mandible. Dx?

focal osteoporotic marrow defect
if this were a focal osteoporotic marrow defect, what would be your next step?

Incisional biopsy is necessary to get definitive dx
Don’t really know why this is here but what do you think it is?

Idiopathic osteosclerosis
What is an area of radiodensity with unknown cause and cannot be identified as anything else?
idiopathic osteosclerosis
New patient that hasn’t had an infection there. Dx?

idiopathic osteosclerosis
What is your possible differential dx?

- Condensing osteitis: associated with an infection
- Idiopathic osteosclerosis: unknown cause
- Focal cemento-osseous dysplasia: will have a radiolucent rim
- Cementoblastoma: fused with the tooth
*bolded pathology is definitive dx
Tooth has Hx of infection. Dx?

condensing osteitis
What is an asymptomatic radiolucent lesion that is usually seen crossing the midline of the mandible?
Central giant cell granuloma
What radiolucent lesion is usually seen in the posterior mandible of women?
Focal osteoporotic marrow defect
What lesion is usually seen across the anterior/midline of the mandible in women?
central giant cell granuloma
Female patient. Non-neoplastic lesion. Dx?

Central Giant Cell Granuloma
What is your differential? Female patient. Asymptomatic.

- Central Giant Cell Granuloma
- Brown Tumor (of hyperparathyroidism)
- Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
- Odontogenic Keratocyst
Upturned eyes and big, plump cheeks. Dx?

Cherubism
What syndrome features odontogenic keratocysts?

Gorlin Syndrome
What is your differential dx?

- odontogenic keratocyst
- aneurysmal bone cyst
- traumatic bone cyst
- Brown’s tumor
Pt recently experienced trauma. What’s your dx?

traumatic bone cyst (AKA simple bone cyst)
What radiographic feature is suggestive of traumatic bone cysts?

Scalloping of bone between the roots
Dx?

Traumatic bone cyst
What is your differential?

- Odontogenic keratocyst
- Traumatic bone cyst
- Aneurysmal bone cyst
- Ameloblastoma
*bolded pathology is definitive
What is an intraosseous blood-filled cavity surrounded by connective tissue lining?
Aneurysmal bone cyst
Why is an aneurysmal bone cyst not a true cyst?
It doesn’t have an epithelial lining. (lined by connective tissue)