Block 1 Drugs Flashcards
(30 cards)
Antacids:
Drugs
Mechanism of Action
Uses
Side effects
- Aluminium hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide (Maalox)
- Calcium carbonate and magnesium carbonate (Rennie)
Buffer gastric acid to raise pH
Used in:
- Heartburn and indigestion
- Acid reflux
Side effects:
- Aluminium can cause constipation
- Magnesium can cause diarrhoea
Alginates and Antacids:
Drugs
MoA
Uses
Sodium alginate with sodium bicarbonate and calcium carbonate
Anionic polysaccharides that form viscous gel upon binding with water which floats on top of stomach contents, reducing reflux symptoms & protecting oesophageal mucosa
Also increases viscosity of stomach contents to reduce acid reflux.
Used in:
- Reflux oesophagitis (mild cases, OTC)
H2 receptor antagonists: Drugs MoA Uses
- Ranitidine
- Cimeditine
Competitive inhibition of histamine actions at gastric H2 histamine receptors in parietal cells to decrease acid secretion by up to 90%
Used in:
- Reflux oesophagitis (mild cases)
Side Effects: Cimeditine inhibits many cytochrome P450 enzymes
Proton Pump Inhibitors
Drugs
MoA
Uses
- Lansoprazole
- Omeprazole
Irreversible inhibition of H+/K+ ATPase pump in gastric parietal cells =decreased basal and stimulated acid secretion:
- From the circulation, the pro-drug (lipophilic) traverses the parietal cell and enters the canaliculus.
- In acidic canaliculus, drug is activated and trapped.
- Drug binds to H+/K+-ATPase, irreversibly inactivating it.
- For acid secretion to resume, new pump molecules have to be synthesized (2-3 days)
Used in:
- GORD and Reflux Oesophagitis (all but mild cases)
What classes of drugs are used to treat disorders of acid secretion?
- Antacids and alginates
- Histamine H2-receptor antagonists
- Proton pump inhibitors
Why can NSAIDs cause peptic ulcers?
NSAIDs inhibit prostaglandin production by inhibiting cyclo-oxygenase enzyme. (Prostaglandins E2 and I2 stimulate gastric mucous and HCO3 production and inhibit gastric acid production)
Therefore impair renewal of the gastric mucosal barrier which is needed to prevent it from rapidly mixing with stomach contents allowing stomach acid to cause gastric erosions.
Bulk Laxatives: Drugs MoA Uses
- Methylcellulose
- Isphagula Husk
Polysaccharide polymers not broken down by normal process of digestion. Retain water in the GI lumen, softening and increasing faecal bulk and promote increased motility. Act in 1-3 days.
Uses:
- First line for constipation and IBS
Osmotic Laxatives: Drugs
Saline purgatives
Macrogol
Lactulose
Faecal Softeners: Drugs MoA Uses
- Docusate
- Arachis Oil (enema)
Stimulates water & electrolyte secretion into intestinal lumen; lower surface tension at oil-water interface allowing water and fat to enter stool cause it to soften. Act 3-5 days
Uses:
- Constipation
- Fissures
- Piles
Stimulant Purgatives:
Drugs
MoA
Uses
Bisacodyl (usually suppository)
Stimulates rectal mucosa, resulting in mass movements and defaecation in 15-30 minutes Only short courses should be used
Uses:
- Opioid related constipation.
Senna:
Passes unchanged into colon, where bacterial action releases free anthracene derivatives. Anthracene derivatives are absorbed and have a direct on myenteric plexus to increase intestinal motility (stronger muscle contractions)
Which classes of drugs are purgatives?
Bulk laxatives
Osmotic laxatives
Faecal softeners
Stimulant purgatives
Osmotic laxatives: Saline purgatives
MoA
Uses
- Mg sulphate
- Mg hydroxide
Potent, rapid action (1-2 Bowel prep prior to procedure)
Osmotic laxatives: Macrogols
MoA and uses
Inert polymers of ethylene glycol. Sequester fluid in the bowel
Uses:
- Treatment of faecal impaction in children
- Long-term management of chronic constipation
Osmotic laxatives: Lactulose MoA and uses
Semi-synthetic disaccharide of fructose and galactose- mimicks undigested lactose
Colonic bacteria convert it to its two component monosaccharides which are poorly absorbed. Fermentation yields lactic acid and acetic acid which function as osmotic laxatives.
Acts within 1-3 days
Uses:
- Chronic constipation
- Hepatic encephalopathy
- Negating the constipating effects of opioids.
Oral Rehydration Therapy
Isotonic/hypotonic solution of glucose and sodium chloride
Exploits the ability of glucose to enhance the absorption of Na+ and therefore water
Uses:
- Maintenance of fluid and electrolyte balance, rehydration
Opioid anti-motility agents
- Loperamide
- Codeine
Agonist for mu-opioid receptors in myenteric plexus; increases tone and rhythmic (haustral) contractions of the colon but diminishes propulsive activity. Blocks intestinal muscarinic receptors.
Uses:
- Acute, uncomplicated diarrhoea in adults (adjunct to rehydration therapy)
Side Effects:
- Constipation (chronic use)
- Abdo cramps
- Dizziness
- Paralytic ileus can occur
Loop Diuretics
Drugs
Moa
Uses
Side Effects
- Furosemide
- Inhibits Na+/K+/2Cl- transporter (competes with Cl- binding) reducing NaCl reabsorption in the thick ascending LoH therefore decreased water absorption.
- Causes decreased osmotic concentration in the medulla therefore decreased ADH mediated H20 absorption.
- Increased delivery of NaCl to the DCT causes increased Na+ uptake by principal cells, causing loss of K+ and H+.
- Reduce calcium and magnesium absorption
Bind to plasma proteins, not filtered, but secreted directly into PCT so effective in renal impairment.
Uses:
- Peripheral oedema
- Acute pulmonary oedema
- Resistant HTN.
- Heart failure
Side Effects:
- Hypovolaemia
- Hypotension
- Hyponatraemia/hypokalaemia
- Ototoxicity (high doses)
Thiazide diuretics
Drugs
MoA
Uses
Side Effects
- Indapamide
- Bendroflumethiazide
- Hydrochlorothiazide
- Chlortalidone
Inhibits Na+/Cl- co-transporter in early DCT (compete with Cl- binding) so increasing Na+ in lumen therefore water.
Filtered and secreted so not useful in renal impairment
Uses:
- Peripheral oedema (chronic HF)
- HTN
Side Effects:
- Weak/moderate diuresis,
- Hyponatraemia/hypokalaemia
- Increased plasma uric acid (gout)
- Erectile dysfunction
- Hyperglycaemia
Potassium-sparing diuretics: Aldosterone antagonists
Drugs
MoA
Uses
Side Effects
- Spironolactone
- Eplenerone
Aldosterone antagonist as binds to mineralocorticoid receptor in the late DCT/cortical collecting tubule. Prevents synthesis of ENaC and Na+/K+ATPase activation therefore reduced K+ secretion into the lumen (K+ retained) and reduced Na+ reabsorption and accompanying water.
Uses:
- Chronic HF
- Peripheral oedema
- Ascites caused by liver cirrhosis
- Hyperaldosteronism
- Resistant HTN, in combination with loop/thiazide diuretics to prevent K+ loss.
SEs:
- Hyperkalaemia
- Gynaecomastia
Potassium sparing diuretics: ENaC antagonists
Amiloride
Blockade of sodium reabsorption via ENaC channel (competes for Na binding site) therefore decreases luminal permeability to Na+. Causes reduced K+ secretion into the lumen, therefore K+ retained.
Used in combination to prevent K+ loss from use of loop/thiazide diuretics
Side Effects: hyperkalaemia
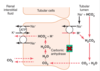
Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
- Acetazolamide
Inhibit carbonic anhydrase in the PCT, preventing it from converting carbonic acid to water and CO2, therefore blocking the absorption of HCO3- and the accompanying sodium and water.
Uses:
- Reduce intraocular pressure (e.g. glaucoma)
Osmotic diuretics
Mannitol
Increases osmolality of glomerular filtrate preventing water reabsorption in the PCT and descending LoH Uses:
- Decrease ICP and intraocular pressure in glaucoma
Why do loop and thiazide diuretics cause hypokalaemia?
Why may alkalosis also occur alongside this?
They increase delivery of NaCl to the distal nephron and decrease blood volume.
This increases K+ secretion by:
- Increasing tubular flow rate (K+ washes away creating high concentration gradient)
- Increases activity of Na+/K+ATPase via increased Na+ therefore more K+ is secreted out of the cells
- Activation of RAAS from decreased blood volume = increased aldosterone therefore more Na+ reabsorption in kidneys = more K+ secreted.
May also cause alkalosis as it can stimulate intercalated cells to secrete H+ so more acid is lost in urine.

Renin Inhibitors
Aliskiren
Prevents renin from converting angiotensinogen to angiotensin I this inhibiting the action of the RAAS system on increasing BP


