Block 1 - Knowing GIS Flashcards
(12 cards)
Explain why GIS is not just a sophisticated software package.
GIS is not only software, but it also involves specific hardware (computer, digitizing table, plotters, etc.) and procedures (techniques and orders for task implementation). According to some people (e.g. Burrough) it also includes the organisational context in which a GIS project is being performed.
What are the basic components of a GIS?
- Computer systems and software;
- Spatial data;
- Data management and analysis procedures;
- People.
Burrough (1986) argues that the organizational context also is essential

What are the strong points of GIS? Or stated otherwise: Why is GIS hot?
Because GIS provides a framework for the efficient collection, storage, analysis and presentation of spatial data and it can be used to analyse and solve all kinds of societal problems that have a spatial dimension.
Why is training to click on the right buttons insufficient for good education in the use of GIS?
Because, as explained in the answers to questions 1, 2 and 3, GIS is much more than pushing the right buttons. You need to formulate a (spatial) question, develop a suitable spatial data model, collect the right data, perform the right analyses and produce adequate maps. Communicating the results is also important. So, there is much more to GIS than just pushing the right buttons.
Give your own definition of GIS and explain why GIS can be difficult to define.
GIS is the whole infrastructure (computer hardware, software, data, knowledge, procedures, analyses and people) that can be used to capture, store, check, integrate, manipulate, analyse and display data that are spatially referenced to earth.
GIS is difficult to define because it comprises many different aspects (hardware, software, data, knowledge, procedures, analyses and people).
Give some examples of questions that could be addressed with GIS when planning new industrial developments.
You can locate suitable spots for new industrial developments by mapping the characteristics of the environment and the planned activities. Examples:
- Transportation routes will be important (to supply and distribute products);
- The environmental impact of different activities can be visualised (e.g. dispersal of noise and pollutants, and the visualisation of safety zones);
- Vulnerable objects (e.g. schools) can be easily identified and visualised.
Describe the relationship between GIS and geographical information science.
Geographical information science is the science behind geographical information systems (GIS). It involves the study of the fundamental issues arising from the creation, handling, storage and use of geographic information, but it also examines the impacts of GIS on individuals and society and the influences of society on GIS.
Explain the difference between data and information.
Information can be considered “data that have been interpreted” or “data with a meaning”. A good example is the difference between a series of letters (e.g., “CAT”) and the meaning of a word (e.g., CAT in English). If you store the letters “CAT” (e.g., on paper or in a text file) they have no meaning as such. However, if you read the letters and interpret them with English language rules and skills, the set of three letters obtains a meaning, i.e., an animal that eats mice and birds.
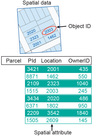
Explain the following term
Spatial data
Data which contain a spatial reference (either in relation to each other or to some arbitrary reference system).

Explain the following term
Attribute data
Data which specify some kind of characteristics or properties of spatial data. For example, a dot on a map can represent a “house” and this house can have “five rooms”.
Explain the following term
Spatial referencing
Specifying the location of an object in relation to a fixed point (which can either be the origin of a raster or a fixed point on earth or another physical entity).

Explain the following term
Spatial entities
Objects with a spatial reference that form an entity because of their (common) attributes (e.g. houses, roads, etc).



