Body Cavities & x-rays Flashcards
(11 cards)
The ventral body cavities and the organs contained therein are lined with slippery membranes
serous membranes or serosae
A serous membrane lining a cavity is called the ___
- There is fluid (serous fluid) in the space between the membranes. You can think of this arrangement of membrane lined cavities and organs by picturing your fist being pushed into a partially inflated balloon. Your fist represents an organ. The part of the balloon clinging to your fist is the visceral membrane which covers the surface of the organ. The outer wall of the balloon represents the parietal serosa, and the air in the cavity is the serous cavity which is filled with serous fluid instead of air. The serous fluid is secreted by both the parietal and visceral serosae. It reduces friction and permits the organs to move easily within their cavities. Think of your lungs. Every time you breath in and out your lungs expand and contract. The pleural cavities with their slippery serosal linings and lubricating serous fluid in between make this possible and pain free. Have you ever had a condition known as pleurisy? In this disease, the pleural membranes become inflamed and stick together by adhesions. This impedes the movement of the lungs and makes it is extremely painful to breath

parietal membrane
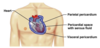
A serous membrane or serosa covering the viscera is called a ___.
visceral membrane
- collectively referred to as the pleura; includes the parietal and visceral pleural membranes
- (Of the ventral cavity)
Pleural cavities
pericardium = the parietal and visceral pericardium
pericardial cavity
peritoneum = parietal peritoneum which lines the walls of the abdominopelvic cavity and the visceral peritoneum which line the organs).
peritoneal cavity
are best suited for examining dense structures like bones, solid tumors, foreign objects, or screening for tuberculosis (a disease in which dense tubercles form in the lungs).
x-rays
A series of transverse sections are stacked one on top of the other, and a computer is used to construct 3-dimensional images that can be rotated to reveal tumors, aneurysms, kidney or gallstones, infections, etc. It is useful when a rapid diagnosis is needed as in acute trauma cases.
CT scan
- makes use of short-lived radioisotopes attached to biological molecules like glucose that are injected into the patient’s body.
- as the radioisotopes are absorbed by the most active cells, gamma rays are emitted. Collecting cameras are positioned around the patient, and they send information to a computer.
- show where the radioactive substance is being most actively taken up by tissues or organs.
- are used to examine patients with brain or heart conditions, or with tumors. Because the amount of “signal” given off is based on the degree of metabolic activity of the tissue or organ,
- are useful for metabolic studies, and mapping biochemical changes taking place in the body during certain activities.
- provide physiological information as well as anatomical.
PET scans
- commonly used for viewing the spine, brain, joints, bones, soft tissues and blood vessels. Some exams may require the administration of an intravenous injection of a contrast agent.
- also yield physiological information. The degree of molecular activity is measured and color coded. Tumors, plaques in blood vessels, tissue and joint injuries, mental disorders, brain changes, blood flow are a few examples of common uses of___
- The are also good for detecting degenerative diseases, and can monitor small changes in blood flow and tissue activity without the use of radioactive tracers.
- DETAIL
MRI
- Of all the techniques, it is the least potentially dangerous to use.
- That’s why its used to look at unborn fetuses to determine if they are healthy and developing properly.
- High-frequency sound waves are reflected from the body’s tissues. The image produced is called a sonogram.
- can be used to produce static or moving images. Besides viewing the unborn fetus, ___ is commonly used to look at blood flow and heart function (echocardiography).
Ultrasound


