breast disorders Flashcards
(54 cards)
inspection of breasts involves
- examines sitting upright and in the supine position
- both arms relaxed, raised, and body leaning forward, hands on hips

list the concerning physical exam findings of breast mass
- hard, gritty texture of breast mass
- immobile
- irregular borders
- > 2 cm
- new or growing
concerning finding on breast exam of nipple discharge
- unilateral
- bloody
- spontaneous discharge
what imaging modalities are used to evaulate breast mass
- mammography -> most useful in women >35
-
ultrasound -> most useful in women < 35
- adjunct ot mammo
-
MRI
- adjunct to mammo and US
What are the normal views taken with mammograms
- CC = cranial cadual view: top to bottom
- MLO = medial lateral oblique
What are concerning findings on mammogram considering a mass
- increased density
- irregular border
- spiculation: lump of tissue with spikes or points on the surface
- clustered irregular microcalcifications
if have clinically suspicious lump, does a negative MRI r/o cancer
No
What is US used for in evaluation of breast cancer
- adjunct to mammogram
- mass cystic or solid
- guide core needle biopsies
what are concerning findings of US for a breast mass
- hypoechoic lesion with ill-defined borders
- mass that is taller than wide
- spiculated margins
what imaging modality is best at demonstrating ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
MRI
biopsies help to determine presence of malignant cells and determine if mass has what receptors
estrogen and progesterone
Fine needle aspiration is ued to aspirate palpable mass/suspected cyst. Is follow up indicated after procedure?
- follow-up 4-6 weeks after aspiration
concerning findings in Fine needle aspiration of breast mass
- recurrence of mass after aspiration
- bloody aspirate
- no fluid is obtained
use of core needle biopsy
- obtain pathologic diagnosis of breast mass
- large 14-18 gauge needle
concerning findings on core needle biopsy and/or sterotactic biopsy on breast mass
- carcinoma
- atypia: abnormal cells
- insufficient specimen
what is a sterotactic biopsy
- provides 3 dimensional view
- evaluate
- microcalcifications, densities, masses
- multiple passes for tissue sampling
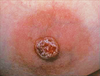
differentiate between incisional and excisional biopsies
- incisional: portion of mass removed
- excisional: entire mass removed
what is mastalgia
breast pain
what is the common presentation of benign mastalgia
- cyclic
- mild
- bilat tenderness and swelling
- common few days preceeding menstrual cycle
what is the concerning findings associated with mastalgia
- persistent
- unilateral pain
- tenderness
What is a ductogram
- used in evaluation of nipple discharge
- cannulation of a single duct with catheter and injection of contrast solution
What are concerning findings regarding nipple discharge
- unilateral
- spontaneous
- localized to single duct
- > 40 yo
- bloody
- associated with a mass
managment of patient with concerning findings regarding nipple discharge
- excisional biopsy of offending duct and mass
- referral to breast specialist
What is Duct Ectasia
- most common cause of nipple discharge
- benign
- multiple dilated ducts in the subareolar space