breast pathology Flashcards
(23 cards)
breast

Medullary carcinoma: high grade/invasive, but good prognosis
well circumscribed on imaging
breast

Micropapillary carcinoma: invasive, worse prognosis due to propensity for lymph nodes
breast

Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
lymph node

Lymph Nodes:
Left: metastatic tumor (yellow arrow) and lymphocytes (white arrow)
Right: Keratin IHC helps detect really focal tumors
breast

Paget’s Dz: epidermal adenocarcinoma (skin involvement), most often associated with in-situ or invasive ductal carcinoma in underlying breast (seen in 2% of mammary CA)
Clinically presents as a rash or erosion of nipple
Histology: glandular tumor cells with pale fluffy cytoplasm, amongst epithelial cells; Her-2/neu + staining in Upper R image.
breast

Inflammatory Carcinoma: tumor invades/obstructs dermal lymphatics leading to redness/warmth/edema of breast, peau d’orange appearance; very poor prognosis
breast

Angiosarcoma: rare complication of radiation (+/-mastectomy); malignant tumor of vascular tissue;
Stewart-Treves = angiosarcoma in skin of lymphedematous area poast-mastectomy/axillary dissection
May present as bruising on the breast

Normal breast: terminal duct/lobular unit (TDLU)

Fibroadenoma: well-defined palpable lump w/ smooth borders in young women (
path: circumscribed stromal/epithelial tumor (fibroepithelial), with bluish-colored stroma and slit-like ductal areas
NO increased risk of CA

Fibrocystic changes: hormone-mediated; seel dilated cysts lined with metaplastic apocrine cells; grossly breasts are lumpy-bumpy;
No increased risk of CA in non-proliferative fibrocystic changes: apocrine metaplasia, fibrotic stroma, cysts
Slight increased risk of CA if proliferative: epithelial hyperplasia, sclerosing adenosis, radial scar

Lactational change/adenoma: see foamy bubbly cytoplasm secreting lipid/protein. Adenomas are well circumscribed, palpable, mobile masses with benign epithelial elements. No increased risk of CA

Gynecomastia: proliferation of stroma and ducts (also hyperplasia), but no lobules/acini

Breast Implant Capsule: see silicon/saline implant in center, surrounded by a fibrous pseudocapsule; also see macrophages/histiocytes with ingested silicon

Fat necrosis: seen with trauma, s/p surgery; presence of anuclear fat cells, with inflammatory infiltrates; can calcify and scar and be mistaken for CA, so have to look at closely.

Proliferative Fibrocystic Change: Usual Ductal Hyperplasia (UDH); benign, low risk of CA;
see ducts full of proliferating cells that are hyperplastic but otherwise normal appearing (not malignant)

Papilloma: fibrovascular stalk; can see bloody discharge from infarction; slight cancer risk 1.5-2x; grossly see bloody nipple discharge, usually non-palpable

Radial Scar: see radiating architecture that can mimic CA (radiographically and pathologically); really hard to dx on bx and usually require special stains

Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS):
green arrow: normal cells
yellow arrow: tumor cells
SEe expanded ducts filled with cells with larger nuclei/nucleoli, mitotic figures, but contained still within the basement membrane

DCIS: yellow arrow pointing to a comedonecrosis (area of high grade necrosis, usually calcifies); all DCIS tumors are bound by cell membrane

Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma:
yellow arrows: DCIS w/ calcification
green arrows: invading ductal carcinoma; see jagged/stringy appearance of stroma due to malignancy
bottom R photo: FNAB stain (doesn’t differentiate in-situ from invasive)

Infiltrating ductal carcinoma; see malignant epithelial infiltrates amongst fat cells and stroma;
desmoplastic stroma (yellow arrow)
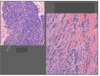
LCIS ( green arrow); contained within basement membrane
Infiltrating Lobular Carcinoma (red arrows): see single-file lines of cells; can see loss of Ecad on IHC, which prevents cells from forming round globules.
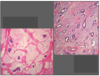
Left: Mucinous Carcinoma
Right: Tubular Carcinoma
both have “Good” prognosis


