CARD 44- Pharm: Anticoagulant, Platelet Inhibitor and Thrombolytics Flashcards
(45 cards)
- What is the MOA of Low molecular weight heparin (LMW)?
- What drug is an example of it
- What effect does it have on factor Xa? Thrombin?
- What are its drawbacks? advantages?

Describe the MOA and PK for Fondaparinux

What are the GP IIb/IIIa Receptor Antagonists?
ATE GP

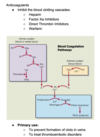
What are the steps of Hemostasis?
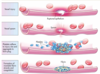
What inhibitor platelet aggregation drug does this describe?
Blocks ADP receptors on platelets

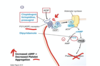
What is the MOA of Heparin?

What are the Pharmacogenomic Considerations: for Warfarin

What is the MOA for Warfarin?

What are the ADP Receptor Antagonists?
Clones Prepared to be ADePt
Tony the Tiger reversed
Ticagrelor is reversible

What inhibitor platelet aggregation drug does this describe?
Blocks formation of TxA2
Aspirin
What are the DDIs and ADRs for aspirin?

Describe the PKs and ADRs for GP IIb/IIIa Receptor Antagonists

How does aspirin affect Cox-1 vs Cox-2?

What are the ADRS for Warfarin?
Describe Warfarin reversal

What are the “substances”?


Where is heparin found?
What are the types of Heparin?

What are the PKs for Warfarin?
What do you need to monitor?
What is it used for?

What are the DDIs and ADRs for ADP Receptor Antagonists?

What are the ADRs of Direct thrombin inhibitors?

What are the uses and PKs for Fibrinolytics/Thrombolytics?

What is the MOA for GP IIb/IIIa Receptor Antagonists?

Describe the MOA, PK, and ADRs for Rivaroxaban

What are the 2 substances responsible for stimulating platelet aggregation?

What is aspirin used for?
What are its PKs?