Cardio - Biochemistry - Fatty Acids; Cholesterol Transport Flashcards
(211 cards)
Which carbon on a fatty acid is the α carbon?
The β carbon?
The ω carbon?
α - carbon 2
β - carbon 3
ω - last carbon
Dissect what each part of this name means:
20:5(Δ5,8,11,14,17) Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
20 carbons
5 double bonds
unsaturated (-enoic)
double bonds at carbons 5, 8, 11, 14, and 17

Dissect what each part of this name means:
18:1(Δ9) Octaecenoic acid
18 carbons
1 double bond
unsaturated (-enoic)
double bond starting at carbon 9

What type of omega fat is this?

Omega-3
(double bond 3rd carbon if you start at the end [omega - ω])
Describe the difference in energy storage timeframes between triglycerides (triacylglycerols) and glycogen.
Glycogen = Short-term energy (< 12 hrs)
Triglycerides = Long-term energy (> 12 hrs)
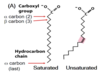
Describe the relative membrane fluidity of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids.
Saturated = less fluid (can pack closely)
Unsaturated = more fluid (kinks don’t pack tightly)
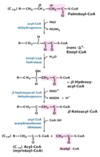
Explain the structure of a 16:0 fatty acid.
It is a saturated FA with 16 carbons and no double bonds
How would you distinguish saturated vs. unsaturated fatty acids using common nomenclature?
Saturated = “anoic acid”
(e.g. 18:0 octadecanoic acid)
Unsaturated = “enoic acid”
(e.g. 18:1(Δ7) trans-7-octadecenoic acid)
What pathologic conditions are implicated with a high consumption of unsaturated fats (e.g. lauric (12:0), myristic (14:0), palmitic (16:0), or stearic (18:0) acid)?
Increased risk of atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, and CVA
Describe the recommended consumption of omega(ω)-fatty acids ratios.
Omega-6 and omega-3 between a 1:1 and 4:1 ratio of consumption, respectively.
What are some example health benefits of Omega-3 FA consumption?
Protective against:
CVD, unhealthy inflammatory responses, poor neuronal responses in brain and retina, CVA, cancer
Describe the structure of palmitic acid in regards to number of carbons and number of double bonds.
And palmitoleic acid?
And stearic acid?
Place an asterisk next to the saturated fats.
16: 0 - saturated*
16: 1 - monounsaturated
18: 0 - saturated*
Describe the structure of oleic acid in regards to number of carbons and number of double bonds.
And α-linolenic acid?
And linoleic acid?
18: 1 - monounsaturated
18: 3 - polyunsaturated (ω-3)
18: 2 - polyunsaturated (ω-6)
Name a few ω-3 fatty acids.
α-linolenic,
eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA),
docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
Name a few ω-6 fatty acids.
Linoleic acid,
arachidonic acid
Identify if each of the following is either an ω-3 or ω-6 fatty acid (identify the two that are essential with an asterisk):
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
Linoleic acid
α-linolenic
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
Arachidonic acid
ω-3
*ω-6
*ω-3
ω-3
ω-6
How do you distinguish the type of omega acid between Linolenic acid and linoleic acid?
Linolenic acid - 1st “n” is 3 letters away from the end = ω-3
Linoleic acid - 1st “n” is 6 letters away from end = ω-6
True/False.
Most naturally occuring double bonds in fatty acids are trans double bonds.
False.
Most are cis but processing creates trans double bonds
(extra unhealthy ‘trans fats’)
True/False.
Too many ω-3 fatty acids outcompete ω-6 fatty acids for enzymatic rate limiting steps and are often the cause of decreases in the postitive effects associated with ω-6 fatty acids.
False.
Too many ω-6 fatty acids outcompete ω-3 fatty acids for enzymatic rate limiting steps and are often the cause of decreases in the postitive effects associated with ω-3 fatty acids.
From what fatty acid are prostaglandins derived?
Arachidonic acid (ARA) (an ω-6 fatty acid)
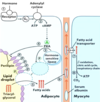
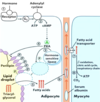
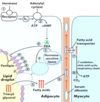
Which fatty acid stored on a triacylglycerol molecule is often the unsaturated one?
How are fatty acids freed from storage for usage when needed?
The one attached to the second carbon on the glycerol backbone;
they are hydrolyzed from the glycerol backbone (and released from their triglyceride storage form)

Describe the functions of triacylglycerols (triglycerides).
- Long-term energy storage
- Cushioning for organs
- Thermal insulation (thermogenin and brown fat)
- Absorption and transport of fat soluble vitamins (A,D,E,K)
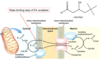
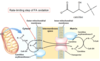
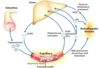
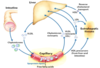
As dietary lipids are ingested and pass into the intestines, how are the gallbladder and pancreas involved in their digestion?
What hormone triggers these reactions?
CCK (cholecystokinin) is released from the intestinal mucosa
–>
causing bile (gallbladder) and lipase (pancreatic) secretion
How is dietary fat broken down in the gut?
Cholecystokinin causes bile/lipase secretion
–>
Bile emulsifies the fat
–>
Lipase cuts fatty acids off the triacylglycerols (triglycerides)
–>
Intestinal mucosa take up the fatty acids