Cardiology Flashcards
(66 cards)
Define Orthopnea
Difficulty breathing in the recumbent position (supine)
Define PND
Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnoea = Patients awaken after 1–2 hours of sleep because of acute shortness of breath
Define Trepopnea
Positional dyspnea that is generally noted in either (one) the left or the right lateral decubitus position Due to disease of one lung, one major bronchus, or chronic congestive heart failure
Define Platypnea
Dyspnea that occurs only in the upright position
Define Hemoptysis
Coughing up of blood
Define Cheyne-Stokes respiration
Respiration characterized by a rapid deep-breathing phase, followed by periods of apnea
Define Stable angina
predictable pattern of angina onset and offset that is stable over time
Define accelerated angina
Angina that occurs at lower levels of exertion or that takes longer to resolve with rest or nitroglycerin; although accelerated angina fits the definition of unstable angina technically, it usually occurs over a longer period and is probably caused by progression of atheromatous coronary disease without plaque rupture.
Define Unstable angina
A change in the patient’s normal pattern of angina onset or offset, probably related to plaque rupture
Define ACS
Acute coronary syndrome. Although this could include STEMI, the term is commonly used to denote unstable or accelerated angina and NSTEMI.
Define Myocardial stunning
Prolonged depressed function of viable myocardium caused by a brief episode of severe ischemia (myocardium can recover with time if recurrent ischemic events are prevented)
Define Hibernating myocardium
Chronically depressed function of viable myocardium as a result of severe chronic ischemia (which can be reversed by revascularization)
Where can a PA catheter be inserted through?
Can be placed via the jugular, subclavian, or femoral veins
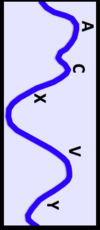
What chambers (in what order) does a PA catheter traverse to measure a wedge pressure?
The RA, RV, PA, and then to PCWP (pulmonary capillary wedge pressure)
What are the normal filling pressures measure by PA catheter?
1) RA pressure or Central venous pressure (thoracic vena cava) = 0–8 mmHg
2) RV Pressire = 15–30 / 0–8mm Hg
3) PA Pressure = 15–30 / 3–12 mmHg
4) PCWP = 3-12 mmHg
What is the PCWP?
Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (aka PAOP, PC pressure, wedge pressure) It is the approximation of the LA and LV pressures during ventricular filling (LVEDP - end diastolic pressure)
How is the PC pressure obtained?
1–1.5 mL of air is pushed into the balloon port of the PA catheter while the PA tracing is watched. When the PA tracing is lost and the PCWP identified, the inflation is discontinued.
What is the danger of overinflating the balloon?
PA rupture, which can be fatal
What is the PCWP useful for?
For determining the intravascular volume status of the patient (i.e., PCWP >20 volume overloaded; PCWP <3 volume underloaded)
How is CO calculated?
Cardiac Output = [HR (beats/min)] * [stroke volume (mL/beat)]
(figure divided by 1000 to get L/min instead of mL)
What is the normal CO?
5 ± 1 L/min
How is CI calculated?
Cardiac Index = Cardiac output/Body Surface Area
What is the normal CI?
3 ± 0.5 L/min/m2
What is the Levine sign?
Clenched fist over the midsternum