Cardiovascular Pathophysiology Flashcards
(11 cards)
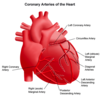
Name the arteries of the heart.

Mechanisms of cardiovascular disease?
- Failure of the Pump
- Obstruction to Flow
- Regurgitant Flow
- Shunted Flow
- Disorders of Cardiac Conduction
- Rupture of the Heart or Major Blood Vessel
Normal Ventricular Wall Thickness?
Right: 0.3-0.5cm
Left: 1.3-1.5cm
Normal Cardiac Weight?
Females: 250-300g
Males: 300-350g
What’s the difference in pathology in these pictures?

Left: Hyaline arteriosclerosis from benign essential hypertension. Deposition of materials around arterioles.
Right: Hyperplastic arteriosclerosis associated with malignant hypertension. “Onion skin appearance.” Proliferation of SMCs around arterioles.
Describe the pathology of atherosclerosis.
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory and healing response to arterial wall and endothelial injury.
- Endothelial Injury/Dysfunction
- Mechanical denudation, immune complex deposition, irradiation, chemicals
- Hemodynamic disturbances, hypercholesterolemia, hypertension, smoking, infectious agents, homocysteine
- Lipoprotein Accumulation
- Lipid accumulation reduced vasodilation ability of vessles
- Hyperlipidemia increases O2 free radicals –> NO decay
- Monocyte Adhesion and Formation of Foam Cells
- O2 free radicals –> oxidies LDL
- Ingested by macrophages = foam cells
- Oxidized LDL –> increases release of growth factors, cytokines and chemokines that increases monocyte recruitment; cytotoxic to endothelial cells and SMC causing endothelial cell dysfunction
- Platelet Adhesion
- Smooth Muscle Cell Adhesion
- Atherosclerotic lesions are in a chronic inflammatory state (T-lymphocytes)
- Chemokines and growth factors produced promote SMC proliliferation and ECM synthesis
- Converts fatty streak –> mature atheroma
- Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation and ECM Production
- Lipid Accumulation
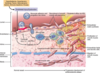
Where do plaques tend to form?
Ostia of exiting vessels
Branch points
Posterior wall of abdomina aorta
(Non-turbulent, laminar flow protects against atherosclerosis.)
What are the dominant lipids in atherosclerotic plaques?
Cholesterol and Cholesterol esters.
At what vascular occlusion percentage does critical stenosis occur?
70%
Risks with acute change of an atherosclerotic plaque?
Aneurysm and Rupture
Occlusion by Thrombus



