Cardiovascular system in health 1 Flashcards
(20 cards)
define autorhythmicity
ability to generate action potention to create contraction.
what are the 2 specialised types of cardiac cells
contractile cells (99%)
Autorhythmic cells
what is different about cardiac autorhythemic cells compared to othe cells muscle/ nerve cell
they do not have resting membrane potential
what do autorhythmic cells display
pacemaker activity
what is the pacemaker potential
slow postive increase of the voltage across the membrane
what is the normal pace maker of the heart
SAN
what are the 4 sites the autorhythmicits located at
SAN
AVN
Bundle of his (atriocentricular bundle)
Purkinje fibers
lable the diagram


what can alter the discarge frequence of the SAN
parasympathetic and sympatheic stimulation
state the 3 functions of the AVN
AV nodes forms the only condcution pathway between the atrail muscle and the bundle of bis and hence the ventricle
AV node introduces delay (100ms) to spread excitation. allowing atrium to empty
AV node cells have developed latent powers of rhythmicity and can take over pacemaking if impulses from SAN fail to reach them.
lable the diagram with the following IONS:
CA2+
NA2+
K+


lable the diagram with the ions in the contractile cells :
NA2+
K+
CA2+
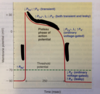

how is action potential create i nthe cardiac contractile cells
- NA+ come in through fast NA+ channels
- Early repolarisation is caused by closure of the Fast NA+ channels
- in platue stage the slow CA2+ channels open while most of the K channel closes
- late repolarisation occures as the CA2+ channels close and K+ channels open
- During the resting potential phase the membrane potential remains constant but ions are s restored to og state.
what does ECG record
Electrical activity in the heart
label the diagram
atrial depolarization
ventricular depolarization
AV node delay
ventricular depolarisatoin/ atrial repolaristion


what is the p wave
atrial depolarization moving towards the recordin electrode
what is q wave
left to right depolarisation of the inerventricular septum moving slightly away fro mthe recording electrode
what is R wave
depolarization of ventricles at the base of the heart moving towards the recording electrode
S wave depolarization of ventricles at the base of the heart moving away from the recording electrode
depolarization of ventricles at the base of the heart moving away from the recording electrode
what is T wave
ventricular repolarization moving in a direction opposite to that of depolarization counts for the usually observed deflection


