Cells & Tissues of Immune System Flashcards
(31 cards)
All immune cells are derived from ____ as a fetus, but then ___ at 7 months.
But the innate immune system is derived from a ___ progenitor and consists of ____
And the adaptive immune system is derived from a ___ projgenitor and consists of
Fetal liver & spleen, but then pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow

Innate - myeloid progenitor; neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, mast cells, macrophages
Adaptive immune system - lymphoid progenitor; B & T cells
B cells mature in the ___
T cells mature in the ___
B cells mature in the bone marrow (where all immune cells originate)
T cells go mature in the thymus
What happens in secondary lymphoid organs like lymph nodes and spleen?
Lymph nodes: B & T cells in lymph meet and get activated
Spleen: B & T cells in blood meet and get activated
Mucosal lymphoid organs - tonsils, adenoids, Peyer’s patches
Name the cell:
Produces antibodies
Cytotoxic and helper functions
Small lymphocyte
B cell
T Cell

Name the cell:
Activates T cells
Initiates adaptive immune responses
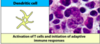
Name the cell:
Fully differentiated form of B cell that secretes antibodies

Name the cell:
Expels parasites from the body byer leasing histamine and other active agents

Name the cell:
Kills cells infected w certain viruses

Name the cell:
circulator precursor cell to a macrophage

Name the cell:
phagocytosis and killing microorganisms
Neutrophils make up the majority of leukocytes!
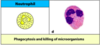
Name the cell:
Phagocytosis & killing microorganisms
Activation of T cells and initiation of immune response

What cell…
- Kills antibody coated parasites through release of granule contents?
- Controls immune responses to parasites?
- Is involved in platelet formation, wound repair?

Lymphocyte maturation (B cell in bone marrow, T cellin thymus) is antigen-independent.
What happens in lymphocyte maturation in BOTH T and B cells?
- Acquire antigen-specific cell surface receptors
-
Elimination of auto-reactive lymphocytes, especially T cells
- If they aren’t killed, then –> autoimmunity
T cell maturation
- Immature T cell interacts with cortical thymic hormones (thymosin, thymulin, thymopoietin)
- Acquires a T cell receptor (TCR) heterodimers (mostly TCR aB)
- CD3 is the signaling component of TCR
- Establish a phenotype
- At first cells have neither: CD4-, CD8-
- Then, they get both: CD4+, CD8+
- Then, one gets turned off: CD4 for helper, CD8 for cytotoxic
- Recognize the processed antigen presented by APCs on an MHC
B cell maturation
(not in lecture)
- Acquire B cell receptor: IgM
- (This receptor is the same antibody that the B cell is going to secrete when activated)
- Recognize and bind the native (unprocessed) antigen
- Clonal proliferation creates memory cells & plasma cells
Lymphocyte activation is antigen-depedent
B cells recognize native antigens
T cells recognized processed antigens presented by APCs as peptide fragments guided by MHC
–> Recognition leads to clonal proliferation
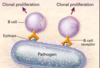
Lymphocyte recirculation
- Enter lymph nodes via endothelial vein
- Exit efferent lymphatics, enter afferent lymphatics to go to next node in the chain (sampling them)
- Reenter circulation via thoracic duct
Lymph node: filters lymphs, supported by reticular network of __ and ___.
B cells are located in the ___
T cells located in the ___
Plasma cells migrat eto the __ to secrete antibodies
Supported by follicular dendritic cells and macrophages.

B cells - cortex
T cells- paracortex
Plasma cells go to the medulla to secrete antibodies
_____ pushes lymph nodes through vessels
___ prevent back flow
___ and ___ can crawl into lymph nodes
Muscle contraction pushes lymph through vessels
Valves prevent backflow
Macrophages & hematopoietic dendritic cells can crawl into lymph nodes to present pathogens to T cells –> clonal proliferation –> new cells and antibodies exit via efferent lymphatic vessel

Two types of dendritic cells:
Follicular dendriic cells: stroma cells in the B cell zones
Hematopoietic cells: immune cells in the T cell zone
All antibodies start as ___, then antibody class switching occurs in the ___ of a lymph node.
Start as IgM
Class siwtching in the apical light zone of the germinal center

The spleen filters blood.
Red pulp vs white pulp
-
RED PULP (sinuses & cords) - non immunologic
- Removes cellular debris (effete)
- Convert hemoglobin to bilirubin
- Release iron into circulation for reutilization
-
WHITE PULP - immunologic
- T cells packed around a central arteriole, forming the periarteriolar lymphoid sheath (PALS)
- B cells organized into primary and secondary follicles, producing antibodies (IgM)
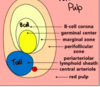
Name some lymphoid tissues
Gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT)
Bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue (BALT)
Epithelium has cytotoxic T cells
Lamina propria has immune cells





