Ch. 17 pt 2 Flashcards
(132 cards)
how does salmonella present clinically
acute - anorexia, abd pain, bloating, N/V, bloody diarrhea w/ short asymp phase –> bacteremia & fever w/ flu-like symp
abd pain may mimic appendicitis
erythematous maculopapular rash (Rose spots)
systemic- extraintestinal complication = septic arthritis, abscess, osteomyelitis, encephalopathy, meningitis, seizures, endocarditis, myocarditis, pneumonia & cholecystitis
what is the pathogenesis of ischemic bowel dz
what variables determine the severity of the dz
two phases:
- initial hypoxic injury
- reperfusion injury
severity:
- severity of vascular compromise
- time frame
- vessels affected (more proximal, more significant)
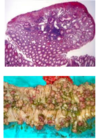
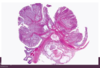
What is the morphology of shigella
L colon (but ileum may be involved)
abundance of M cell in dome epithelium overlying Peyers Patches
mucosa = hemorrhagic, ulcerated & pseudomembrane
histology of early cases similar to self-limited colitides (like Campylobacter colitis)
tropism for M cells, aphthous ulcers similar to Crohns dz

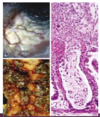
What is the pathogenesis of colon CA
- APC/B-catenin/Wnt path –> classic adenoCA sequence (80% sporadic mutations)
- Microsatellite instability (MSI) path –> defect in DNA mismatch repair
both paths = accumulation of multiple mutations but differ in genes involved & mechanism by which mutations accumulation
epigentic events - MC = methylation induced gene silencing –> enhance progression along either path

which etiologies of colon CA cause sesile serated adenomas & mucinous adenocarinoma
DNA mismatch repair defect
- MYH-associated polyposis = AR
- Hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer - R-side = AD
- Sporadic CA (10-15%)- R side
&&&
hypermethylation = Sporadic CA (5-10%) - R side
How does salmonella cause infection
very few vaible strains cause infxn
= absence of gastric acid, in ind w/ atrophic gastritis or those on acid-suppressive therapy
penetrates SI mucus layer –> transverses the intestinal epithelium thru M cell on Peyer’s patches –> causes Peyers patches in terminal ileum to enlarge & elevations –> hyperplasia –> points of intussusception Mesenteric LN =enlarged
what are characteristics of Schistosoma
*know!!!*
from snail –> ingested
adult worms residing w/i mesenteric veins
sxs by trapped eggs w/i the mucosa and submucosa
granulomatous immune rxn –> bleeding and obstruction
–> SCC bladder
–> cirrhosis (2nd MCC)
what are freq abnormalities in the SI an LI
what are the causes
malabs & diarrhea: disrupt normal h2o and nutrient transport
infectous & inflam disorders: intestinal bacteria 10x # of eukaryotes in the body
Colon = MC site of GI neoplasia in the Western pop
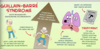
Campylobacter spp.:
geography
transmision
epidemiology
GI site
reservoir
symptoms
complications
high income countries
poultry, milk, contaminated water, other foods - food poisoning
sporadic__, children, travelers
colon
farm animals
water/bloody diarrhea- (travelers diarrhea)
reactive arthritis (pt w/ HLA-B27), guillain-barre syndrome, erythema nodosom
when do you begin regular surveillance colonoscopies
age 50
younger is african american or FHx
polyp removal reduce the incidence of colorectal adenocarcinoma
What are diagnostic tests used infectious enterocolitis
selective serologic testing (giardia Ag)
fecal leukocytes (evidence of invasion)
fecal lactoferrin
stool culture
assays for toxins (C. diff toxin)
stool for ova & parasites
Lactose def = lactose cant be broken down to glu and galac, so it stays in lumen and exerts osmotic forces to attract fluid & cause diarrhea
what are the 2 types of lactose def
- congenital: mutation in gene encoding lactase; _auto re_c; explosive diarrhea w/ watery, frothy stool & abd distention w/ milk ingestion
- aquired: downreg of lactsoe gene expression; native american, african american, chinese; may present after enteric viral/bacteral infxn
(Bx is unremarkable for biochem defect)
Which dz’s have defect of only transepithelial transport
carcionoid syndrome
Abetalipoproteinemia

what are the steps of MMR carinogenesis (10-15 % sporadic & HNPCC)
what are characteristics of intestinal hookworm
penetrate skin –> develop lungs –> migrate to trachea & swallowed
suck blood & reproduce in the duodenum –> multiple superficial erosions, focal hemorrhage, and inflammatory infiltrates
Chronic infxn leads to iron deficiency anemia
neoplasia in IBD are related to..
duration of dz - > 8-10 yo
extent of dz - pancollitis > chance than if only L side dz
neutrophilic response: active inflam
(acquired conditions predispose to CA; chronic inflam, DALM = dysplasia associated lesions or mass (aka precursor lesions) & immune def)
What are characterisitics of V. cholerae
comma-shaped, gram (-)
India & Bangladesh, areas of natural disaster
cause cholera
transmitted in shellfish, contaminated H2O (fecal-oral)
Severe cases: ‘rice water diarrhea’ with fishy odor ==> dehydration
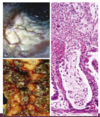
label this

what is the epidemiology of Colon Cancer
highest incidence = North america - bc dietary factors = low fiber, high fat/refined carbs
USA- 2nd MC cause of cancer death
peak incidence = 60-70 yo (rarely under 50 UNLESS HNPCC!)
use of ASA & NSAID –> prevention (inhibit COX-2)
What are characterisitics of obstructions due to adhesions
MC obstrution in USA
most often = acquired (surgery, trauma, intra-abd infxn, endometriosis)
healing –> fibrous bridge that creates loops where material can get lodges btn the bowel & adhesion
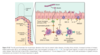
When/How do the SI and LI form embryonically
=4th & 5th wk
quickly outgrow the space –> entire midgut herniate into the umbilical cord - form loop
rotate –> pulled back for midline closure

Wht are characterisitics of adenovirus
common cause peds diarrhea & immunocompromised diarrhea
droplet/close contact transmission
SI bx show epithelial degeneration but more often non specific villous atrophy & compensatroy crypt hyperplasia
nonspecific sxs - resolve after 10 days
what are other causes of chronic colitis
what are characteristics of each
diversion colitis: blind colon segment bc of SRG resulting in ostomy; develop numerous mucosal lymphoid follicles; cure = re-anastamonsis
microscopic colitis: both types = watery diarrhea w/o wt loss; collagenous-in mid-age F; lymphocytic- in celiac dz & auto immune dz
graft-vs-host dz: after allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; crypts severely destroyed; watery diarrhea may become bloody in severe cases
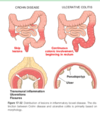
what is the distinction between UC and Crohns primarily based on?
what are these characterisics for crohns dz
distribution & morphology
- MC: terminal ilieum, ileocecal valve, cecum (40% limited to SI & 30% SI & LI); multiple, sharply delineated areas (skip lesions)
- intestinal wall = thickened/rubbery bc transpural edema, inflam, submucosal fibrosis & hypertrophy of muscularis propria
- extensive transmural dz –> creeping fat - mesenteric adipose tissue extend over the serosal surface