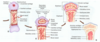
Ch 7 - Skeletal System Flashcards
(95 cards)
Skeletal System functions (5)
- support
- protection
- movement
- storage(calcium+phos,fat,min) 5. blood cell production(marrow-rise to RBC) - hematopoiesis
Bone, cartilage, tendons ligaments are what type of tissue
CT
extracellular matrix contains:
- collagen (glue producing tough ropelike protein) 2. proteoglycans (protein+polysaccharides) 3. water 4. minerals
4 types of bone
- long bone (longer than are wide, levers for muscles; femur, humerus, ulna/radius)
- short bone (approx. as broad as they are long, glide; wrist, ankle, carpal bone, talus)
- flat bone (thin, flat, proect organs; skull, ribs, scapula, sternum, internal and extrernal table(compact) with dipole (calncellous bone)
- irregular bone (vertebra, facial, sphenoid)
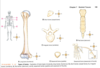
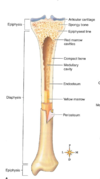
5 parts of large bone - with description and label diagram
- diaphysis
- epiphyses
- articular cartilage
- periosteum
- medullary cavity
- endosteum

diaphysis
long central shaft, provides support, hollow so not as heavy
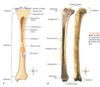
epiphysis & process
ends of long bone, spongy/cancellous filled with red marrow, upon development, seperated from diaphysis by epiphyseal line
- epiphyses are seperated from diaphysis by epiphyseal plate (growth plate) which is made of cartilage (until it fills in) and allows for bone growth-in kids,teens
- cartilage later is replaced by bone (ossification) and forms epiphyseal line-adults
- region is now called metaphysis
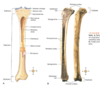
articular cartilage
covers the ends pf epiphysis, where bone connects to bone (joint)
periosteum
outer surface of bone (except for joing surfaces)
dense CT
contains blood vessels and nerves – PAIN ex shin splints
contains enthesis - where tendons imbed themselves into the periosteum of bone, connected by Sharpy’s fibers (stitch tendons into the p of bone)
contains osteoblasts (repair/remodeling of formation of bone = dynamic)

medullary cavity
tubelike, hollow space in diaphysis
“marrow cavity” - adults bone, filled with CT rich in fat,WBC = yellow marrow
in youth, starts as mainly red marrow, blood cells
in adult, red marrow confined to proximal ends of long bone
endosteum
lines medullary cavity and spongy bone
is a thinner CT membrane
contains osteoblasts (repair/remodeling of formation of bone = dynamic)
Compact bone
mostly solid matrix
blood vessels enter and exit bone
waste and nutrients in/out through the haversian canal system

cancellous bone
aka spongy bone, trabeculae beams filled with marrow
lacy network of bone, small marrow-filled spaces
Location: mainly epiphysis of long bone
Forms: interior/intter part of bone
Gives stregnth without added withed

osteoblasts
small “bone-forming” cells
cells that secrete osteoid (matrix)
osteogeneic stems cells in endosteum undergo cell division – form osteoblasts
ossification - formation of bone by osteoblasts
remove calcium from blood and gives to forming bone
osteoclasts
large “bone-reabsorbing” cells
responsible for active erosion of bone minerals
as minerals and calcium are dissolved during bone erosion, they are reabsorbed back into blood (original source) - osteoclasts returns to blood
cartilage
CT (hyaline - rings of ribs, lungs, bronchi; elastic - ear,opening respitory tract; fibro - dense CT)
sustains great weight when covering articulating bone surgaces
shock absorbant
NO canal system of blood vessels penetrate
chondrocytes
scatter mutrients and O2 to cartilage via diffusion through the perichondrium
only healthy cells in cartilage matrix that makes collegan and proteglycans
appositional vs interstital(longitudal) growth in cartilage
longitudal/intersistial, “enodenous growth” - occurs WITHIN cartilage tissue, childhood/adolescence, chondrocytes divide and secrete additional matrix, which can happen b/c soft nature of cartilage tissue.
appositional growth, “exogenous growth” - occurs OUTER surfaces of cartilage tissue. beyond adolescence and throughout adult life. chondrocytes in deep layer of perichondrium divide and secrete additional matrix, which is placed on surface of cartilage, wihch causes it to increase in size. Bone grows in DIAMETER, where scoliosis is imporant to manage
bones develop baby 2 processes
intermembranous and endochondral ossification - result in compact and cancellous bone
intramembranous ossification
within CT membrane
where flat bones and formed within fibrous membrane
endochondral ossification
“bone formation in cartilage”

4 phases of bone healing
- blood vessels ruptured, swelling
- bleeding
- fracture hematomas, fibrocartilage splints bone
- develops into granulation tissue containing inflammatory cells, fibroblasts, bone/cartilage forming cells, capillaries
- Formation of bony callus tissue
- Replaced with normal bone
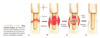
PTH vs calcitonin
hormones secreted by PTG and thyroid gland
primary homestatic mechanisms for blood regulation fo Ca+
High blood Ca+ level(hypercalcemia) - calcitonin released, breakdown bone matrix decreases, Ca+ in blood decreases
Low blood Ca+ level(hypo) - PTH released, breakdown increases, Ca+ in blood rises

avascular necrosis
death of bone tissue due to lack of blood flow
- can lead to breaks in bones and sometimes collapse
“snow cap sign”, “bite sign”, sclerosis
can happen when there is fracure or dislocation
predisposing factors: cortisone shots