Ch 8: Cells in Their Environment Flashcards
(28 cards)
What is the plasma membrane?
>The plasma membrane forms the boundary between the internal environment of the cell, the cytoplasm and its external environment.
- It is selectively permeable (that is, controls the movement of substances into and out of cells).
- physical and chemical properties enable it to control the exchange of materials and messages
What are functions and some benefits of the plasma membrane?
Plasma membrane regulates the internal environment.
- Complex chemical reaction including respiration and photosynthesis facilitated
- Enzymes can only perform their tasks within narrow temperature and pH ranges.
- Hydrogen ion concentrations kept within strict limits to maintain suitable cytoplasmic pH.
- Toxic waste products are removed to ensure they do not interfere with chemical reactions in the cytoplasm.
What is a cell wall?
>provides strength and support to cells of plants, fungi and most algae
- permeable - allows the passage of almost all materials
What is the fluid mosaic model?
membranes as a lipid bilayer with the ability to flow and change shape, specialised proteins are embedded in the lopid in various patterns

What is the phospholipid bilayer?
- a phosphate group on the head makes this end hydrophilic (able to absorb water or dissolve in water)
- the fatty acid tails are hydrophobic (water avoiding or unable to dissolve in water).
- when these molecules spontaneously form a bilayer, the fatty acid tails turn inwards, away from the watery environment and cytoplasm, and towards each other, rather like salad oil forming a film on the surface of water.

How do lipids affect the phospholipid bilayer?
- Cholesterol interferes with interactions between the lipid tails, making the membrane (of animals) more flexible.
- In plants and bacteria, phytosterol not cholesterol increases membrane flexibility.
- The lipid components of all membranes, whether from plants, animals or bacteria, provide membranes with the unique properties of being flexible and able to repair themselves. This allows cells to change shape and grow.
List the different types of membrane proteins:
- Adhesion proteins link cells together to maintain both the three-dimensional structure and the normal functioning of tissues.
- Transport proteins act as passageways that allow specific substances to move across the membrane. i.e. the rapid movement of ions across the membrane when a nerve is stimulated.
- Membrane proteins are also involved in cellular communication. Receptor proteins bind hormones and other substances that cause changes to the cell’s activities.
- Membrane recognition proteins: called glycoproteins because they combine with a sugar molecule, are unique to each individual. They act as markers, called antigens, which allow the immune system to distinguish between the body’s own ‘self’ cells, and foreign invaders (‘non-self’ cells).
What is transport and what are some types?
> movement that does not require energy
- diffusion
- facilitated diffusion
- osmosis
What is the difference between active and passive transport?
- Movement of particles down a concentration gradient, from where they are in high concentration to where they are in low concentration, is passive and does not require energy.
- Movement of particles up a concentration gradient, from where they are in low concentration to where they are in high concentration is active and requires energy.
What is diffusion?
- passive movement of molecules from a high to low concentration of that substance
- occurs when a gradient exists and continues until the particles are distributed evenly (equilibrium) - where particles will continue to move but at equal rates in all directions
- takes place in gases and liquids
- increasing the concentration gradient/heating the particles will increase the rate of diffusion
- across membranes:
- small uncharged particles i.e. oxygen, water and carbon dioxide move easily through the plasma membrane of a cell

What is facilitated diffusion?
- form of diffusion that requires a substance to be attached to a specific carrier molecule to move across a membrane
- charged particles i.e. sodium and chloride ions, and relatively large molecules i.e. glucose and amino acids, do not pass through the phospholipid bilayer readily. In the plasma membrane, certain proteins assist such particles to diffuse into the cell. This process is called facilitated diffusion.
- Two types of protein are involved in facilitated diffusion: carrier proteins and channel proteins.
- Carrier proteins bind to specific molecules on one side of the membrane, change shape and release the substance on the other side. i.e. the glucose transporter protein, which is located in the plasma membrane of all mammalian cell types and carries glucose in either direction, depending on the direction of the concentration gradient.
- Channel proteins form narrow passageways through which small ions can diffuse rapidly from a high ion concentration to a lower ion concentration. Only ions of a specific size and shape can pass through a particular channel protein.

What does a carrier protein look like in action?

What does a channel protein look like in action?

What is osmosis and what is does water do?
>special type of diffucion, the movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane from a region of low to high concentration
- Plasma membranes are selectively (differentially) permeable, meaning that water molecules pass through them easily, but solutes do not i.e. if the concentration of water molecules inside a cell is lower than the concentration outside, water will diffuse into the cell, until a balance or equilibrium is reached.
- Water is the medium in which biochemical processes take place, water transports materials in solution, it helps keep cells in shape and it forms the fluid that bathes tissues. Water is described as the universal solvent.
Define solution, solvent and solute:
Solution (mixture of particles) = solvent particles + solute particles
- High-concentration solution = low concentration of solvent + high concentration of solute
- Low-concentration solution = high concentration of solvent + low concentration of solute
solvent = substance in which another substance can be dissolved in
solute = substance that can be dissolved in another solution
Define iso / hypo / hyper - tonic:
isotonic: if the fluids inside and outside a cell are of equal solute concentration, the external solution is said to be isotonic (‘iso’ = same) to the cells; water molecules jostle on both sides of the membrane, moving in both directions equally.
hypotonic: when cells are surrounded by a solution that contains a lower solute concentration than their cytoplasm, the external solution is said to be hypotonic to the cells (‘hypo’ 5 lower). Water molecules will diffuse through the membrane into the cells.
hyper: the reverse applies if the cells are surrounded by a solution of higher solute concentration; the external solution is hypertonic (‘hyper’ 5 higher) to the cells and water molecules will diffuse out.
What is osmosis like in animals?
- The cells of unicellular eukaryotes and multicellular organisms, such as animals, are surrounded only by a plasma membrane, unlike the cells of plants, fungi and bacteria, where a cell wall surrounds the plasma membrane. Hypertonic solutions, like fresh water, pose a special problem for these organisms. Water moving into their cells by osmosis can cause the fluid plasma membrane to swell and eventually burst, killing the organism.
- Unicellular: i.e. Amoeba that live in fresh water have important regulatory mechanisms to combat these problems. They are able to remove excess water by forming little pools of water in cytoplasmic organelles called contractile vacuoles. When these vacuoles stretch to a certain point, they contract and expel the water.
- multicellular: cells are bathed in a isotonic extracellular fluid, to keep the isotonic balance, the solute concentration in the extracellular fluid is controlled by the concentration in of solutes in blood plasma, which in turn is controlled by the kidneys.
- If an intravenous drip contains salty water - the plasma surrounding blood cells becomes hypertonic, water will move out of the cells by osmosis and, in a process called crenation, they will shrink and become crinkled. The resulting small, shrunken blood cells tend to stick together, clogging small veins and arteries, and preventing oxygen reaching body tissues. If enough blockages occur, the results may be fatal.
- It is equally dangerous for an intravenous solution to be hypotonic. If the blood plasma is diluted by water, the blood cells will swell and burst. This condition is called haemolysis and it can seriously reduce the amount of oxygen being transported to body tissues. Because of these effects of osmosis on animal cells, it is important that the solute concentration of blood plasma is regulated by the kidneys.

What does an amoeba look like?

What is osmosis like in plants?
> plant cells vacuole membrane (tonoplast) is differntially permeable, it contains cell sap that is rich in solutes
- turgor: important as supports plant and maintans their shape and form i.e. when soaking limp vegetables to make them crisp
- plasmolysis: i.e. what can happen to plants on a hot dry day

What is active movement and what are the different types of it?
> when the movement of substances across a membrane requires energy
types:
- active transport
- endocytosis
- exocytosis
What is active transport?
> the process whereby cells actively transport subtances across a membrane from a low concentration to a high concentration of the substance (up their concentration gradient).
- Membrane transport proteins, similar to those responsible for facilitated diffusion, use energy from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to move molecules/ions up their concentration gradient
- As these carrier proteins work in only one direction, they effectively act as one-way valves.

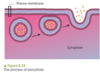
What is endocytosis?
> the movement of substances into a cell from the environment via vesicle formation
- phagocytosis: process that engulfs solids
- process macrophages use in defending the body against disease, it why they are called phagocytes
- pinocytosis: bulk transport of liquids into a cell inside a vesicle

What does phagocytosis look like?

What is exocytosis?
> movement of substances from a cell to the environment via vesicle formation
- a membrane bound vesicle moves to the plasma membrane, fuses with it and then releases its contents to the exterior of the cell
- Specialised animal cells produce a variety of substances, such as hormones, mucus, milk proteins and digestive enzymes, which have important functions elsewhere in the organism. This is also true for plants, where particular cells are specialised to produce products that need to be relocated. These include growth regulators, toxins to ward off predators and macromolecules for use elsewhere. In all these cases, exocytosis is involved.