Changes in Plasma Volume and Renal Control of Blood Pressure Flashcards
(204 cards)
Where is the water in the body located?
- Intracellular fluid (ICF)
- Extracellular fluid (ECF)
What seperates the intracellular fluid and the extracellular fluid?
The cell membrane
What tightly regulates the volumes of the ICF and ECF?
Their ionic compositions and osmosis
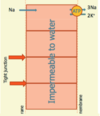
What is ECF volume determined largely by?
The concentration of NaCl
How can the kidney maintain the ECFs volume within a very narrow margin?
By regulating the excretion of NaCl
What must the kidneys balance?
The amount of Na+ excretion with ingestion
What is the process of matching Na+ secretion with ingestion called?
Sodium balance
What is meant by a patient being in positive balance?
Na+ excretion is less than intake
What happens when a patient is in positive balance?
ECF expansion
Why does a positive sodium balance lead to ECF expansion?
Na+ is retained in the body, primarily in the ECF. Water is drawn out of the nephron causing a corresponding increase in volume
What happens as a result of ECF expansion?
With respect to blood volume and arterial pressure
- Blood volume increases
- Arterial pressure increases
Oedema may follow
What is meant by a patient being in negative balance?
Na+ excretion is greater than intake
What happens when a patient is in negative balance?
ECF contraction
Why does a negative sodium balance lead to ECF contraction?
The Na+ content of the ECF decreases, so less water is drawn out of the nephron, so ECF volume decreases
What happens as a result of ECF contraction?
With respect to blood volume and arterial pressure
- Blood volume decreases
- Arterial pressure decreases
Do changes in Na+ affect ECF osmolarity?
No
Why doesn’t changes in Na+ balance affect ECF osmolarity?
If the concentration of Na+ in the ECF increases, then volume increases. The increase in volume gives increased cardiac output, and increased Na+ excretion
What % of Na+ is filtered in the glomerulus?
100%
What % of Na+ is reabsorbed in the PCT?
67%
What is meant by glomerular tubular balance?
The proportion of Na+ reabsorbed is always the same, regardless of the actual amount that is filtered
What does autoregulation do?
Prevents GFR from changing too much
What is the result of glomerular tubular balance?
If any changes in GFR occur, it blunts out the Na+ excretion response
Is Na+ reabsorption an active or passive process?
Mainly active
What drives Na+ reabsorption?
3Na-2K-ATPase pumps on the basolateral membrane