Chapter 11 Alkanes Flashcards
(90 cards)
Alkanes are [____] hydrocarbons; that is, they contain only carbon–carbon single bonds.
saturated hydrocarbons
A hydrocarbon that contains one or more carbon–carbon double bonds, triple bonds, or benzene rings is classified as [____].
an unsaturated hydrocarbon
We often refer to alkanes as [____] because the physical properties of the higher members of this class resemble those of the long carbon-chain molecules we find in animal fats and plant oils
aliphatic hydrocarbons


Identify the class

arenes
Identify the class

alkynes
Give angle.

109.5o
What kind of formula is this?

Line Angle formula
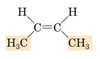
What kind of isomers are these?

Constitutional isomers
also called
structural isomers
with constitutional isomers.
What formula is the same?
What formula is different?
Same molecular formula.
Different structural formula.
Give name:

isopropyl
(give shape)
isopropyl
(give shape)
Give name:

(give name)

isobutyl
(give structural formula)
(give name)

sec-butyl
(give structural formula)
Give name

tert-butyl
(give structural formula)
Give name:

cis-1,2-dimethylcyclopentane
give name:

trans-1,2-dimethylcyclopentane
Which has the higher boiling point?


Identify the higher boiling point.








Identify the type of fatty acid.

saturated fatty acid
Identify the type of fatty acid.

monounsaturated fatty acid