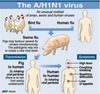
Chapter 13 Flashcards
(66 cards)
Virus literally means…
Poison
Viruses are __________ _________ parasites
Obligate, Intracellular
How big/small are Viruses?
20 – 1000 nm
What is the goal of Viruses?
To reproduce
Why are most organisms susceptible to viral infection?
we think viruses are ancient and have been evolving along with organisms
Pandora Virus
opens Pandora’s box and makes us change the way that we think about viruses and change perspectives of evolutionary biology
Bacteria can be filtered to _____________.
Sterilize
Do Viruses contain DNA, RNA or Both
Either DNA or RNA
Characteristics
- contain a single type of nucleic acid, either DNA or RNA,
- contain a protein coat,
- multiply inside living cells using the cellular machinery
- cause synthesis of specialized structures that transfer viral genetic information.
Why are antiviral drugs difficult to develop?
target host machinery!
Virion
complete, fully-developed infectious viral particle
How are Viruses classified?
- morphology,
- type and structure of genetic information
- replication strategy.
Does a Virion contain DNA, RNA or Both?
?
Viral genetic information is encoded in _________?
- double-stranded DNA,
- single-stranded DNA,
- dsRNA
- ssRNA
In what SHAPE is viral genetic info. encoded?
linear, circular, or segmented
How many nucleotides (base pairs) will you find in a virus?
from thousands to 250,000
What is the CAPSID?
protein coat that protects the nucleic acids of viruses
*accounts for most of the mass of a virus
What is a CAPSOMERE?
protein subunits that assemble to form the capsid
What are some viral capsids coated with?
an envelope of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids.
*Although the proteins of the envelope are encoded by viral genes
*some of the envelope’s components derive from host-cell constituents
Disadvantages of a viral envelope?
sensitive to drying out
Viral SPIKES
What are they used for (by scientists)?
Purpose of them?
- to identify certain viruses
- facilitate host-cell attachment
*facilitates specific host-cell interaction through hydrogen bonds and ionic bonds

How could we exploit viruses to treat human disease?
?
Phage Therapy
the therapeutic use of bacteriophages to treat pathogenic bacterial infections
Gene Therapy
Treating a disease by replacing abnormal genes