Chapter 34: Thyroid Disease + Surgery Flashcards
(58 cards)
How much does the thyroid weigh?
30 g
Where does the isthmus usually lie?
Midline
Main anatomical points of thyroid:
Right lobe, left lobe, isthmus
What is most common issue with thyroid gland?
Enlargement
Parathyroid glands: How many? Size?
4 4 mm x 6 mm
Most common source of problems in parathyroid gland?
Endocrine disorder
Which nerves are contiguous with the thyroid gland?
RLNs
What increases risk for injury or loss of nerve?
Thyroid malignancy
What adjunct is necessary when operating on thyroid?
Nerve testing and NMB monitoring
Range of testing device for RLNs in thyroid surgery?
0.5-2 mA
The thyroid gland is contiguous with what airway structure?
Trachea
What is a goiter?
Enlargement of thyroid gland
Where can goiters grow? What are they called in their respective positions?
Can grow in chest (intrathoracic) or in neck (extrathoracic)
What is your biggest concern regarding goiters?
They tend to shift the trachea and therefore shift the glottis.
What type of disease may deviate and/or compress the trachea?
Thyroid disease
In what thyroid case would the patient require intubation post-operation?
Only the patient with tracheal malasia would remain intubated for 2-5 days as the surrounding tissue healed.
Immediate risk to thyroid disease/surgery?
Interruption/injury to one/both RLNs
This tool is used for:

Mediastinoscopy
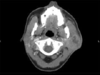
Condition demonstrated in this picture

Intrathoracic goiter

Mediastinoscopy
Pathway of the RLNs:
Transverses chest (right vs. left difference)
Ascends in neck lateral to airway
Which cranial nerve is contiguous with thryoid gland?
Vagus (CN X)
Origin of RLNs?
Vagus nerve (CN X)
What anatomical structures protect RLNs?
Protected in larynx by thyroid cartilage