Clinical Anatomy of Cranial Nerve Testing Flashcards
(35 cards)
List the ‘12’ Cranial Nerves and their modalities
CN I olfactory nerves (special sensory)
CN II optic nerves (special sensory)
CN III oculomotor nerves (motor & parasympathetic)
CN IV trochlear nerves (motor)
CN V trigeminal nerves (CN V1 & V2: sensory only*; V3 is sensory & motor*)
CN VI abducent nerves (motor)
CN VII facial nerves (special sensory; motor & parasympathetic)
CN VIII vestibulocochlear nerves (special sensory)
CN IX glossopharyngeal nerves (special sensory; sensory; motor & parasympathetic)
CN X vagus nerves (sensory; motor; parasympathetic)
CN XI spinal accessory nerves (motor)
CN XII hypoglossal nerves (motor)
Which part of the CNS do each originate from?
Forebrain - I, II
Midbrain - III, IV
Pons - V
Pontomedullary junction - VI, VII, VIII
Medulla - IX, X, XII
Spinal cord - XII
Label from view superior to cranial fossae

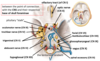
Through which cranial fossa do each of the Cranial nerves leave the crainial cavity?
Anterior fossa - CN I
Middle fossa - CN II, III, IV
Posterior fossa - CN V - CN XI
Foramen magnum - CN XII
Describe the divisions of the trigemninal nerve
3 divisions
- Ophthalmic (CNV1) – sensory
- Maxillary (CNV2) – sensory
- Mandibular (CNV3) – sensory and motor
Describe and detail the course of the Trigeminal Nerve
CNS connection:
The only CN to attach to the pons (laterally, midway between midbrain & medulla)
Intracranial Course:
inferior to the edge of the tentorium cerebelli between the posterior and middle cranial fossae
Skull Base Foramen:
- CN V1 - superior orbital fissure
- CN V2 - foramen rotundum
- CN V3 - foramen ovale
Extra-cranial Course:
- Sensory axons from all 3 divisions course, from the superficial and deep structures of the face, posteriorly, towards their respective base of skull foraminae
- motor axons from CNV3 course from the foramen ovale towards the skeletal muscle they supply
Label the somatic sensory innervation to the head


CN V1 deep sensory territory?
- bones & soft tissues of the orbit (except the orbital floor & lower eyelid)
- the upper anterior nasal cavity
- all paranasal sinuses (except the antrum)
- the anterior & posterior cranial fossae
CN V2 deep sensory territory?
- the lower posterior nasal cavity
- the maxilla & maxillary sinus (antrum)
- the floor of the nasal cavity/palate
- the maxillary teeth & associated soft tissues (gingivae & mucosae)
CN V3 deep sensory territory?
- the middle cranial fossa
- the mandible
- the anterior 2/3rds of the tongue
- the floor of the mouth
- the buccal mucosa
- the mandibular teeth & associated soft tissues
Name and detail the muscles of masstication
Close Jaw
- Masseter
- Temporalis
- Medial Pterygoid
Open Jaw
-Lateral Pterygoid
Describe the origin and attachments to the muscles of masstication
Masseter - Angle of mandible - Aygomatic arch
Temproalis - coronoid process of mandible - lateral aspect of neurocranium
Medial Pterygoid - Medial mandible - Pterygoid plates fo the sphenoid bone
Lateral Pterygoid - Condyle of mandible and articular disc of TMJ - Pterygoid plates of the spenoid bone
List the key areas for testing the sensory afferent of the Trigmeninal Nerve
- Ophthalmic (CNV1):
- forehead, upper eyelid & tip of nose
- Maxillary (CNV2):
- mid-cheek, lower eyelid, upper lip & nostril of nose
- Mandibular (CNV3):
How would you clinically test the Sensory afferent of the trigemnial nerve?
- Ask the patient to close their eyes
- Gently brush the skin in each dermatome with a fine tip of cotton wool
- Ask the patient to tell you when they feel their skin being touched
- Compare the 2 sides
How would you clinically test the motor efferent of the trigeminal nerve?
- Palpate the strength of contraction of the masseter & temporalis by asking patient to clench their teeth
- Ask the patient to open their jaw against resistance
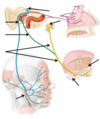
Describe and detail the course of the Facial Nerve
- Connection to the CNS
- Intracranial course
- Base of skull exit
- Extracranial Course
Connection to the CNS
-anterolateral at pontomedullary junction
Intracranial course
-directly into internal acoustic meatus in the posterior cranial fossa
Base of skull exit
- internal acoustic meatus of the temporal bone
- stylomastoid foramen
Extracranial Course
-most somatic motor axons pass into the parotid gland then into 1 of the 5 branches that supply the muscles of facial expression
Label the diagram of facial nerve course


Label the facial nerve diagram

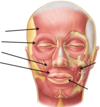
Label and detail the muscles of facial expression

Describe and detail the course of the Glossopharyngeal nerve
- Connection to the CNS
- Intracranial course
- Base of skull exit
- Extracranial Course
Connection to the CNS
-lateral aspect of superior medulla oblongata
Intracranial course
-directly towards jugular foramen in the posterior cranial fossa
Base of skull exit
-junction between temporal bone & occipital bone – jugular foramen
Extracranial course
-axons mainly pass to or from the tongue and palate
List the modalities of the glossopharyngeal nerve
General somatic sensory
Special sensory
Visceral afferent
Somatic motor
Parasympathetic (secretomotor)
List the general sensory of the glossopharyngeal nerve
- the posterior 1/3rd of the tongue
- the mucosa of most of the nasopharynx
- the mucosa of all of the oropharynx
- the mucosa of some of the laryngopharynx (some overlap with CN X territory)
- the palatine tonsil
- the eustachian tube
- the middle ear cavity
List the special sensory of the glossopharyngeal nerve
•the vallate papillae (with taste buds) of the posterior 1/3rd of the tongue
List the visceral afferent of the glossopharyngeal nerve
visceral afferent to the carotid sinus baroreceptors & the carotid body chemoreceptors
(carotid massage relevance)






