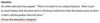Commodity Portfolio Management Flashcards
(94 cards)
Commodity Characteristics
- Raw material or a primary agricultural resource, that can be purchased or sold for production and/or consumption.
- These tangible assets have no credit risks and many of them are most of time liquid.
- Commodities are traded on open markets throughout the world.
- Nearly no commodity price can go to zero, because commodities are always likely to be worth something to somebody. Only Power Prices have traded below 0.
1 Commodity BasicsBasics

1.1 Commodity Differentiation Basics

Physical Oil Market- 1.1 Commodity Differentiation Basics


1.1 Commodity Differentiation – Commodity Exchanges

1.1 Commodity Differentiation - Top Energy Products at the CME

1.2.1 Commodity Volatility
Driven by Supply and Demand, Inventories, Transport Costs, Logistics, Speculation, Sentiment, Geopolitical Factors.

1.3 Commodity Market Participants
The Actors on Commodity Exchanges

1.3.1 Types of Futures Market Participants

1.3.2 Commodity Trading Firms


1.4 Commitment of Traders Report
What does speculative participation look like as a fraction of open interest?
- The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) publishes a weekly commodity futures/option report which breaks down the total open interest as of each Tuesday’s settlement.
-
The reports are released every Friday and provide market participants insight on how open interest is distributed among different groups of traders
- – (Producer/Merchant/Processor/User, Swap Dealers, Managed Money, and Other Reportable).
Open Interest
- number of long and short positions in a specific contract which have not been liquidated or offset by an opposing purchase or sale by the same participant.
- Non-commercials are momentum, or positive feedback traders
- commercials are on average contrarians (net short).


1.5 Open Interest
Open Interest
- number of long and short positions in a specific contract which have not been liquidated or offset by an opposing purchase or sale by the same participant.
- Increasing open interest figures are considered supportive of the underlying price trend.
– they may indicate market strength during periods of rising prices,
– or the support of a downward trend during periods of market weakness.

2 Rationale for Investing in Commodities

2.1 Diversification Benefits of Commodities


2.2 Commodities as a possible Inflation Hedge
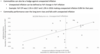
3 Commodity Investment Vehicles
Commodity Assets Under Management by Type and Sector
- A niche asset class emerging from a cyclical downturn

3.1 Commodity Forwards

Value at Risk


The Benefits of Forward Curves


Term Structure of Commodity Prices

Arbitrage

3.1 Commodity Forwards–Synthetics

Basis Risk

3.1 Commodity Forwards–Several types of basic risk

3.1 Commodity Forwards–Financial Transaction Example: Power Station