Congenital diseases Flashcards
(100 cards)
What chromosomal trisomy is seen in Patau syndrome?
Trisomy 13
What chromosomal trisomy is seen in Edwards syndrome?
Trisomy 18
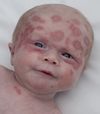
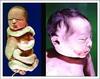
A prominent occiput, low-set ears and clenched fists is associated with which trisomy?
Edwards syndrome

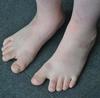
What are these?

Rocker-bottom feet
Seen in Edwards and Patau syndromes
Microcephaly, microphthalmia and polydactyly are characteristic of which trisomy?
Patau
{ } is a congenital GI disorder characterised by megacolon due to a lack of ganglion/enteric nervous plexuses as a result of failed neural crest cell migration
Hirschsprung disease
{ } is a trisomy disorder associated with duodenal atresia and Hirschprung disease
Down syndrome
{ } is a congenital duodenal malformation that results in early bilious vomiting and proximal stomach distention due to failure of the duodenum to recanalise
Duodenal atresia
The double bubble sign is characteristic of which condition?
Duodenal atresia/stenosis
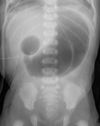
What is the most common congenital anomaly of the GI tract?
Meckel diverticulum

{ } is a GI diverticulum that is 2 inches long and found 2 feet from the ileocecal valve in 2% of the population
Meckel diverticulum
What causes Meckel’s diverticulum?
Partial failure of the vitelline duct/omphaloenteric duct to obliterate

What is the most common cause of congenital adrenal hyperplasia in infants?
21ß-hydroxylase deficiency
Enzyme required for cortisol production
What is the main problem in children with a congenital diaphragmatic hernia?
Pulmonary hypoplasia
Compression by the herniated viscera prevents development of the heart and lungs
Confers a high mortality if present
What is the most common cause of nasal polyps in children?
CF

What is the VACTERL association?
A combination of congenital diseases associated with mesodermal defects
V - vertebral anomaly
A - anal atresia
C - cardiac anomaly
T - tracheosophageal fistula
E - esophageal atresia
R - renal anomaly
L - limb malformation
What is the function of CFTR proteins in sweat glands?
Reabsorption of Cl-
Decreased reabsorption → increased sweat chloride
What is the role of CFTR proteins in epithelial tissue?
Facilitate the diffusion of Cl- into secretions → water follows by osmosis
In CF secretions are thick and cannot be cleared
Why can CF cause diabetes?
Retention of digestive enzymes → destruction of islet cells
What is the most common cause of urinary obstruction in the newborn male?
Posterior urethral valves
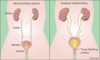
What is the most common cause of vesicoureteral reflux?
Congenitally short ureter → inadequate closure of the uterovesicular junction
Often resolves with age as the ureter grows in length
Why do children with congenital adrenal hyperplasia have hyperandrogenism?
Impaired cortisol production → high ACTH → adrenal hyperplasia + increased androgen production
How does hyperandrogenism present in females with congenital adrenal hyperplasia?
Clitoral enlargement
Precocious puberty
Virilisation (male secondary sexual characteristics)
How does hyperandrogenism in males with congenital adrenal hyperplasia present?
Precocious puberty