Connective Tissue Flashcards
(72 cards)
All connective tissue (stroma) is composed of:
- relatively few cells and a relatively large amount of intercellular material (ECM).
In connective tissue, the intercellular material is
known as:
- extracellular matrix (ECM)
The ECM has two components:
- fibers (such as collagen or elastin)
- ground substance (such as proteoglycans)
What is the principle cell of connective tissue?
- fibroblasts
What do fibroblasts produce?
- the fibers and the ground substance in the ECM
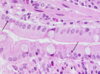
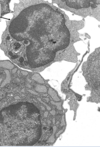
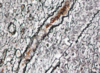
The right arrow is marking out:

connective tissue
The bottom black arrow is pointing to:
basement membrane
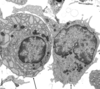
The right arrow is marking out:

connective tissue
Tendons and ligaments are considered what type of connective tissue?
- dense regular connective tissue
Tendons connect:
- muscle to bone
Tendons are composed of:
- collagen with just a little elastic tissue.
Ligaments connect:
- bone to bone
Ligaments are composed of:
- Collagen but with more elastic fibers since we want both stretch and the ability to return to the original shape
The polyanionic properties (abundance of negative charged molecules) of ground substance enable it to:
- hold Na+ ions and water in the connective tissue and thus resist compression.
Functions of connective tissue:
- Mechanical support.
- Exchange of metabolites.
- Storage of energy reserves.
- Endocrine functions.
- Thermogenesis.
- Protection against infection.
- Repair after injury.
Functions of white adipose tissue:
- stores triglycerides that can be metabolized to produce energy
- possible endocrine function
Functions of brown adipose tissue:
- heat generation/thermogenesis
Why do connective tissues usually heal well after injury?
- Fibroblasts and mesenchymal cells in CT have a great capacity to proliferate in response to injury.
Cells that reside in connective tissue:
- fibroblasts, mesenchymal cells, adipocytes
Cells that migrate through connective tissue:
- white blood cells
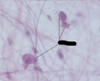
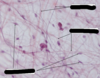
Shape of fibroblasts:
- Fusiform shape, long and tapered
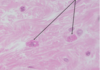
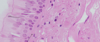
What are the arrows pointing to?

fibroblasts
Structural features of fibroblasts:
- Well-developed RER and Golgi.
- Central nucleus, prominent nucleolus.
- Fusiform shape, long and tapered.
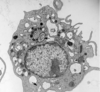
What is the cell in the top left?
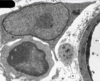
fibroblast cell