CVS: ECG Flashcards
(19 cards)
What is an ECG?
(Electrocardiogram)
Electrical activity of the heart (depolarisation + repolarisation) recorded from electrodes postition on the surface of the body.
It provides:
- timing + direction of cardiac events (atrial & ventricular depolarisation, ventricular repolarisation - atrial repolarisation takes place the same time as v.repolarisation)
- rate/rhythm disturbances (tachy (fast heart rate)/bradycardia (slow heart rate); sinus rhythm; arrhythmias)
- conduction of abnormalities (A-V conduction time)
- mass of active myocardium (ischaemic areas)
Describe this image
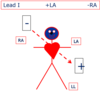
Depolarisation moving away from a positive electrode (+ towards a negative electrode) gives a downward deflection
Depolarization moving towards a positive electrode (+ away from negative electrode) gives an upward deflection

Describe this image

Depolarisation moving towards a negative electrode gives a downward deflection
Depolarisation moving away from a negative electrode gives an upward deflection
What is Repolarisation?
Like depolarisation, what are the rules of repolarisation when reading a ECG?
Reverse electrical charge change to depolarisation
Repolarisation towards a positive electrode produces a downward reflection
Repolaarisation away from a positive electrodes gives a upward deflection
During excitation of the heart, waves of depolarisation move through atria + ventricles in various directions.

How can we get a recorded potential difference?
Mean electrical vector represents the sum of all of the individual vectors at a given instant in time.
Describe the cardiac cycle

Action potentials in epicardial cells have a ___ duration than in endocardial cells.
Why is this?
Shorter
They are last to depolarise + first to repolarise

What is the first wave called?
P wave
Atrial depolarisation
Irrespective of its polarity
What is the last/final wave called?
T wave
Ventricular repolarisation
What is the first positive wave after a P wave called?
R wave
What is the negative wave after a P wave but before an R wave called?
Q wave
What is the negative wave after an R wave called?
S wave
What is the positive wave after an S wave called?
R’ wave
Label each wave on the diagram

‘Classical’ ECG recorded with +ive at apex

Label each wave on the diagram

ECG recorded with +ive at right shoulder

Where is the viewing positiong of a Lead II?


What is the viewing position of Lead I?

What direction does ventricular repolarisation travel?
Opposite direction to depolarisation

Which wave/s represent ventricular depolarisation?
QRS


