Cytology - Neoplasia Flashcards
(56 cards)
How are neoplasms classified on cytology?
•Depending on cell origin - mesenchymal, epithelial and round cells.
Mesenchymal cells = (2)
- Cells forming tissues that are considered “soft” tissues or connective tissues, stromal tissues.
- Embryologically derived from the mesoderm (e.g. fibrocytes, adipocytes, cartilage, etc.)
Epithelial cells = (2)
- Cells derived external surfaces, mucus membranes, parenchymal organs and organ surfaces, glandular tissues.
- E.g. mammary gland cells, skin liver cells, urinary bladder lining, etc.
Round cells =
•Composed of five discretely occurring cells (lymphocytes, plasma cells, histiocytic cells, mast cells, Transmissible Venereal Tumour).
Cell anatomy diagram. (4)
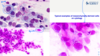
What are the cytological features (morphology and characteristics) of mesenchymal cells?


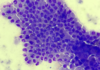
What are the cytological features of epithelial cells?




What are the cytological features of round cells?

Five types of round cell tumours. (5)
- 1). Mast cell tumour.
- 2). Lymphoid tumours.
- 3). Plasmacytic tumours.
- 4). Histiocytic tumours.
- 5). Transmissible Venereal Tumour.
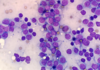


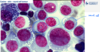
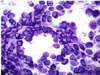

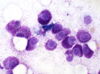
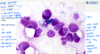
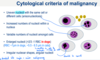
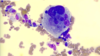
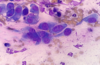
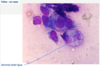
Cytological criteria of malignancy. (11)
- 1). Variable sizes of cells = anisocytosis.
- 2). Variable sizes of nuclei = anisokaryosis.
- 3). Multinucleate cell.
- 4). Anisokaryosis within the same cell.
- 5). Cell crowding/disorganisation.
- 6). Nuclear moulding.
- 7). Enlarged nuclei = macrokaryosis.
- 8). Micronuclei/satellite nuclei/lag chromatin.
- 9). Increased numbers of mitotic figures - abnormal cell divisions.
- 10). Hyperchromatic (dark cytoplasm).
- 11). Significant dilation of cytoplasm + displacement of nucleus = signet ring appearance.
Karyon =
•Nucleus.
Anisocytosis =
•Variable sizes of cells.
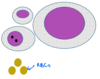
Anisokaryosis =
•Variable sizes of nuclei.
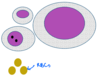




Macrokaryosis =
•Enlarged macrokaryosis - diameter is more than two neutrophils.