Deductive Geometry Flashcards
How big is angle ABC and which theorem proves this?
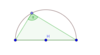
Angle in a Semi-circle Theorem
90° because of the angle in a semi-circle is a right angle.
What do we know about the lengths of line segments a and b and which theorem proves this?
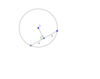
Chords of a Circle Theorem
They are the same size since the perpendicular from the centre of a circle to a chord bisects the chord.
What do we know about the angle α and which theorem proves this?

Radius-tangent Theorem
90° since the tangent to a circle is perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact.
What do we know about the lengths of a and b and which theorem proves this?
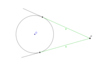
Tangents from an External Point Theorem
They are the same size since tangents from an external
point are equal in length.
What do we know about line AB and which theorem proves this?
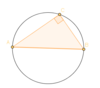
Angle in a Semi-circle Theorem
If line segment AB subtends a right angle at C then the circle through ABC, then it must make a semi-circle. Therefore AB is the diameter of the circle.
What do we know about the angles α and β and which theorem proves this?

Angle at the Centre Theorem
α is twice as big as β since the angle at the centre of a circle is twice the angle on the circle subtended by the same arc.
What do we know about angles α and β and which theorem proves this?

Angles Subtended by the Same Arc Theorem
They are the same size because angles subtended by an arc on the circle are equal in size.
(Less mathy wording is that any angle on the edge of the circle with the same two starting points (also on the circle) are the same size.)
What do we know about angle α and β and which theorem proves this?
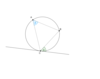
Angle Between a Tangent and a
Chord Theorem
They are the same since the angle between a tangent and a chord at the point of contact is equal to the angle subtended by the chord in the alternate segment.
What do we know about angles α and β and which theorem proves this?
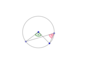
Angle at the Centre Theorem
α is twice as big as β since the angle at the centre of a circle is twice the angle on the circle subtended by the same arc.
What do we know about angles α and β and which theorem proves this?
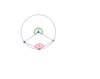
Angle at the Centre Theorem
α is twice as big as β since the angle at the centre of a circle is twice the angle on the circle subtended by the same arc.
What do we know about angles α and β and which theorem proves this?
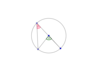
Angle at the Centre Theorem
α is twice as big as β since the angle at the centre of a circle is twice the angle on the circle subtended by the same arc.
What does it mean when two angles are supplementary?
They add to 180°.
What does it mean when angles are complementary?
They add to 90°.

How do you know if a quadrilateral is cyclic?

- All four points can be connected with a perfect circle.
- One pair of opposite angles is supplementary


