Derm Flashcards
What are the 3 most common skin and soft tissue infections? what is included in their differential dx?
Cellulitis Erysipelas Skin abscesses Gout DVT Venous stasis dermatitis (Bilateral)
Skin layers affected in Cellulitis, Erysipelas and Skin abscesses?
cell - deeper dermis and subcutaneous fat
erys - upper dermis and superficial lymphatics
skin ab - upper and deeper dermis
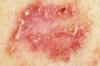
Name skin condition: unilateral presentation raised above level of surrounding skin with clear demarcations b/w involved and uninvolved skin. Non-purulent. acute onset of sx.
Erysipelas
b-hemolytic strep can present with butterfly rash on face**
pathogen responsible for: erysipelas cellulitis abscesses
ery - B-hemolytic strep
cell - b-hemolytic strep, staph aureus, MRSA
abscesses: sstaph aureus, MRSA
risk factors for Cellulitis, Erysipelas and Skin abscesses?
Skin barrier disruption
Preexisting skin conditions (eczema, impetigo, tinea)
Skin inflammation
Edema due to lymphatic drainage or venous insufficiency (venous stasis presents BILATERALLY)
Obesity
Immunosiuppression
Close contact w/ people w/ MRSA
complications of Cellulitis, Erysipelas and Skin abscesses?
NF
bacteremia and sepsis - blood cx
osteomyelitis - x-rays
septic joint - aspiration
Pasteurella multocida
cat bite
Capnocytophaga canimorsus
dog bite
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
farm animals
Vibrio vulnificus
water borne = step on something at beach
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
must cover if pt is a diabetic
Sporothrix schenckii
rose gardener
Define impetigo
contagious superficial bacterial infection seen most commonly on the face seen in children age 2-5 more common in summer and fall
Primary vs secondary impetigo
primary - direct bacterial invasion of normal skin
secondary - infection at sites of skin trauma
what is the most common bacterial infection in children?
impetigo 3rd most common skin condition in children
Name the skin condition

non-bullous impetigo
Most common form
S auerus
Name skin condition?

bullous impetigo
vesicles enlarge to form flaccid bullae with clear fluid
becomes darker -> rupters leaving thin brown crust
fewer lesions - seen primarily in children
trunk more affected
S.aureus strain that produces a toxin that causes cleavage of superficial skin layer
Nsme skin condition?

Impetigo + Ecthyma
ulcrative form
lesions extend through epidermis to deep dermis
“punched out” ulcers covered in yellow crusts
Group A beta hemolytic strep pyrogenes
Treatment for Impetigo + ecthyma
ORAL
Dicloxacillin 250 mg QID
cephalexin 250 mg QID
erythromycin (penicillin allergy)
clindamycin (MRSA suspected)
Treatment for non-bullous and bullous impetigo?
TOPICALS
mupirocin (bactroban) TID
retapamulin (Altabax) BID
ORAL - if extensive
dicloxacillin
cephalexin
erythromycin (for penicillin allergy)
clindamycin (if mRSA suspected)
Complications of impetigo?
poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis
edema
HT
fever
hematuria
all seen 1-2 wks post infection
MRSA CA vs MRSA HA
CA -
- Sensitive to non-beta-lactam antibiotics
- Initially reported in IVDU
- Most frequent cause of SSTI presenting to US ERs and ambulatory clinics
HA
- Infection that occurs >48 hours following hospitalization
- Leading cause of surgical site infection
- Multidrug resistance
Treatment for MRSA
PO
trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
clindamycin
doxycycline
minocycline
IV
vancomycin
daptomycin
Define clinical presentation of Urticaria
intensley puritic raised erythematous plaques with central pallor
ANY area of body can be affected
waxing and waning (lesions appear and disapper w/in 24 hrs) - more severe at night
sometimes accompanied by angioedema (lips, extremeties, genitals)