Dermatology 1 Flashcards
(84 cards)
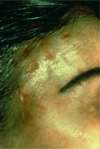
Definition of macule
A flat, circumscribed region of skin with different color or texture (example: freckle)

definition of patch
A large macule (> 1 cm) or a coalescence of macules (example: vitiligo) (like huge areas of depigmentation)

definition of papule**
A palpable, circumscribed change in consistency or contour of the skin (example: acne vulgaris - red zits) A SMALL RAISED AREA

define nodule
A papule larger than 1 cm in diameter (example: neurofibroma)
A LARGE PAPULE

define tumor
A large nodule (example: lymphoma)
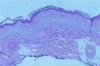
define plaque**
A coalescence of papules (example: psoriasis) COLLECTION OF PAPULES

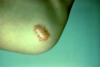
define cyst
An encapsulated nodule filled with soft material (example: epidermal cyst)
define vesicle
A circumscribed, clear fluid filled lesion; a blister (example: Herpes simplex)
(A BLISTER)

define bulla
A large vesicle (example: bullous pemphigoid)

define pustule
A vesicle filled with inflammatory cells (example: acne vulgaris - white head)
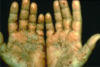
define wheal
A palpable, circumscribed, area of edema with central pallor and peripheral erythema that usually disappears relatively quickly. (HIVES - localized area of swelling. white area surrounded by red)
these are eosinophil mediated processes
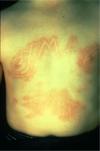
define purpura
Discoloration of the skin due to the presence of blood in the tissue, outside of blood vessels; will not blanch with pressure (example: vasculitis)
* the pinpoint lesions lower in the picture = petechiae

define petechiae
A punctate region of purpura (tiny dots)
define comedo
A plug within a hair follicle canal which is composed of keratin and sebum; a blackhead (example: acne vulgaris)
define milium
A white papule composed of whorls of keratinized epidermal cells beneath the skin surface (example: milia)
those white dots on people’s eyelids
define burrow
A horizontal tunnel in the stratum corneum produced by a parasite (example: scabies)

define scaly
2ndary lesion: Characterized by exfoliation of surface keratin cells (example: psoriasis)
define hyperkaratoidic
2ndary lesions subtype: Having very thick scale (example: icthyosis)
define crusted
2ndary lesions: Displaying dried exudate of fluid and/or cellular components on the skin surface.

define serous
2ndary lesion: Composed of serum or tissue fluid (example: contact dermatitis)
define purulent
2ndary lesion: Containing pus (example: infection)
define hemorrhagic
2ndary lesion: Containing red cells; a scab (example: healing herpes zoster)
define eroded
2ndary lesion: Showing a superficial defect in the skin surface which does not penetrate through the epidermis (example: abrasion)
defne ulcerated
2ndary lesion: Showing a skin defect which penetrates through the epidermis (example: diabetic foot ulcer)
NO DERMIS LEFT